- Inhibitors
- Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
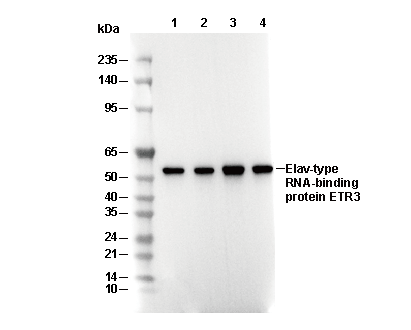
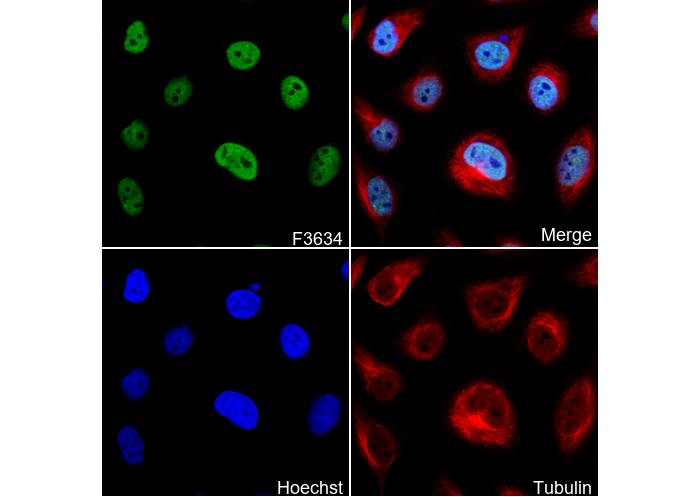
Elav-type RNA-binding protein ETR3 Antibody [M8J19]
Cat.No.: F3634
Application:
Reactivity:
Usage Information
| Dilution |
|---|
|
| Application |
|---|
| WB, IP, IHC, IF, FCM |
| Reactivity |
|---|
| Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Source |
|---|
| Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody |
| Storage Buffer |
|---|
| PBS, pH 7.2+50% Glycerol+0.05% BSA+0.01% NaN3 |
| Storage (from the date of receipt) |
|---|
| -20°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles), 2 years |
| Predicted MW |
|---|
| 54 kDa |
| Positive Control | Human fetal liver; Human brain; Rat lung; K562 cell; HeLa cell; MCF7 cell; C6 cell; NIH 3T3 cell |
|---|---|
| Negative Control |
Exprimental Methods
| WB |
|---|
Experimental Protocol:
Sample preparation
1. Tissue: Lyse the tissue sample by adding an appropriate volume of ice-cold RIPA/NP-40 Lysis Buffer (containing Protease Inhibitor Cocktail),and homogenize the tissue at a low temperature. 2. Adherent cell: Aspirate the culture medium and wash the cells with ice-cold PBS twice. Lyse the cells by adding an appropriate volume of RIPA/NP-40 Lysis Buffer (containing Protease Inhibitor Cocktail) and put the sample on ice for 5 min. 3. Suspension cell: Transfer the culture medium to a pre-cooled centrifuge tube. Centrifuge and aspirate the supernatant. Wash the cells with ice-cold PBS twice. Lyse the cells by adding an appropriate volume of RIPA/NP-40 Lysis Buffer (containing Protease Inhibitor Cocktail) and put the sample on ice for 5 min. 4. Place the lysate into a pre-cooled microcentrifuge tube. Centrifuge at 4°C for 15 min. Collect the supernatant;
5. Remove a small volume of lysate to determine the protein concentration;
6. Combine the lysate with protein loading buffer. Boil 20 µL sample under 95-100°C for 5 min. Centrifuge for 5 min after cool down on ice.
Electrophoretic separation
1. According to the concentration of extracted protein, load appropriate amount of protein sample and marker onto SDS-PAGE gels for electrophoresis. Recommended separating gel (lower gel) concentration: 10%. Reference Table for Selecting SDS-PAGE Separation Gel Concentrations 2. Power up 80V for 30 minutes. Then the power supply is adjusted (110 V~150 V), the Marker is observed, and the electrophoresis can be stopped when the indicator band of the predyed protein Marker where the protein is located is properly separated. (Note that the current should not be too large when electrophoresis, too large current (more than 150 mA) will cause the temperature to rise, affecting the result of running glue. If high currents cannot be avoided, an ice bath can be used to cool the bath.)
Transfer membrane
1. Take out the converter, soak the clip and consumables in the pre-cooled converter;
2. Activate PVDF membrane with methanol for 1 min and rinse with transfer buffer;
3. Install it in the order of "black edge of clip - sponge - filter paper - filter paper - glue -PVDF membrane - filter paper - filter paper - sponge - white edge of clip"; 4. The protein was electrotransferred to PVDF membrane. ( 0.45 µm PVDF membrane is recommended ) Reference Table for Selecting PVDF Membrane Pore Size Specifications Recommended conditions for wet transfer: 200 mA, 120 min. ( Note that the transfer conditions can be adjusted according to the protein size. For high-molecular-weight proteins, a higher current and longer transfer time are recommended. However, ensure that the transfer tank remains at a low temperature to prevent gel melting.)
Block
1. After electrotransfer, wash the film with TBST at room temperature for 5 minutes;
2. Incubate the film in the blocking solution for 1 hour at room temperature;
3. Wash the film with TBST for 3 times, 5 minutes each time.
Antibody incubation
1. Use 5% skim milk powder to prepare the primary antibody working liquid (recommended dilution ratio for primary antibody 1:1000), gently shake and incubate with the film at 4°C overnight; 2. Wash the film with TBST 3 times, 5 minutes each time;
3. Add the secondary antibody to the blocking solution and incubate with the film gently at room temperature for 1 hour;
4. After incubation, wash the film with TBST 3 times for 5 minutes each time.
Antibody staining
1. Add the prepared ECL luminescent substrate (or select other color developing substrate according to the second antibody) and mix evenly;
2. Incubate with the film for 1 minute, remove excess substrate (keep the film moist), wrap with plastic film, and expose in the imaging system. |
| IF |
|---|
Experimental Protocol:
Specimen Preparation
1. Aspirate liquid, then cover cells to a depth of 2–3 mm with 4% Paraformaldehyde diluted in 1X PBS.
NOTE: Paraformaldehyde is toxic, use only in a fume hood.
2. Fix cells for 15 min at room temperature.
3. Aspirate fixative, rinse three times in 1X PBS for 5 min each.
4. Proceed with Immunostaining.
Immunostaining
1. Add theblocking buffer and incubate for 60 min at RT.
2. Prepare primary antibody diluent in antibody dilution buffer as recommended .
3. Aspirate blocking solution, apply diluted primary antibody.
4. Incubate overnight at 4°C.
5. Rinse three times in 1X PBS for 5 min each.
6. Incubate specimens in fluorochrome-conjugated secondary antibody diluted in antibody dilution buffer for 1–2 hr at room temperature in the dark.
7. Rinse three times in 1X PBS for 5 min each.
8. Mount slides usingmounting medium with DAPI and cover with coverslips.
9. For best results, allow mountant to cure overnight at room temperature. For long-term storage, store slides flat at 23°C protected from light.
|
| IF |
|---|
Experimental Protocol:
Sample Preparation
1. Adherent Cells: Place a clean, sterile coverslip in a culture dish. Once the cells grow to near confluence as a monolayer, remove the coverslip for further use.
2. Suspension Cells: Seed the cells onto a clean, sterile slide coated with poly-L-lysine.
3. Frozen Sections: Allow the slide to thaw at room temperature. Wash it with pure water or PBS for 2 times, 3 minutes each time.
4. Paraffin Sections: Deparaffinization and rehydration. Wash the slide with pure water or PBS for 3 times, 3 minutes each time. Then perform antigen retrieval.
Fixation
1. Fix the cell coverslips/spots or tissue sections at room temperature using a fixative such as 4% paraformaldehyde (4% PFA) for 10-15 minutes.
2. Wash the sample with PBS for 3 times, 3 minutes each time.
Permeabilization
1.Add a detergent such as 0.1–0.3% Triton X-100 to the sample and incubate at room temperature for 10–20 minutes.
(Note: This step is only required for intracellular antigens. For antigens expressed on the cell membrane, this step is unnecessary.)
Wash the sample with PBS for 3 times, 3 minutes each time.
Blocking
Add blocking solution and incubate at room temperature for at least 1 hour. (Common blocking solutions include: serum from the same source as the secondary antibody, BSA, or goat serum.)
Note: Ensure the sample remains moist during and after the blocking step to prevent drying, which can lead to high background.
Immunofluorescence Staining (Day 1)
1. Remove the blocking solution and add the diluted primary antibody.
2. Incubate the sample in a humidified chamber at 4°C overnight.
Immunofluorescence Staining (Day 2)
1. Remove the primary antibody and wash with PBST for 3 times, 5 minutes each time.
2. Add the diluted fluorescent secondary antibody and incubate in the dark at 4°C for 1–2 hours.
3. Remove the secondary antibody and wash with PBST for 3 times, 5 minutes each time.
4. Add diluted DAPI and incubate at room temperature in the dark for 5–10 minutes.
5. Wash with PBST for 3 times, 5 minutes each time.
Mounting
1. Mount the sample with an anti-fade mounting medium.
2. Allow the slide to dry at room temperature overnight in the dark.
3. Store the slide in a slide storage box at 4°C, protected from light.
|
| IHC |
|---|
Experimental Protocol:
Deparaffinization/Rehydration
1. Deparaffinize/hydrate sections:
2. Incubate sections in three washes of xylene for 5 min each.
3. Incubate sections in two washes of 100% ethanol for 10 min each.
4. Incubate sections in two washes of 95% ethanol for 10 min each.
5. Wash sections two times in dH2O for 5 min each.
6.Antigen retrieval: For Citrate: Heat slides in a microwave submersed in 1X citrate unmasking solution until boiling is initiated; continue with 10 min at a sub-boiling temperature (95°-98°C). Cool slides on bench top for 30 min.
Staining
1. Wash sections in dH2O three times for 5 min each.
2. Incubate sections in 3% hydrogen peroxide for 10 min.
3. Wash sections in dH2O two times for 5 min each.
4. Wash sections in wash buffer for 5 min.
5. Block each section with 100–400 µl of blocking solution for 1 hr at room temperature.
6. Remove blocking solution and add 100–400 µl primary antibody diluent in to each section. Incubate overnight at 4°C.
7. Remove antibody solution and wash sections with wash buffer three times for 5 min each.
8. Cover section with 1–3 drops HRPas needed. Incubate in a humidified chamber for 30 min at room temperature.
9. Wash sections three times with wash buffer for 5 min each.
10. Add DAB Chromogen Concentrate to DAB Diluent and mix well before use.
11. Apply 100–400 µl DAB to each section and monitor closely. 1–10 min generally provides an acceptable staining intensity.
12. Immerse slides in dH2O.
13. If desired, counterstain sections with hematoxylin.
14. Wash sections in dH2O two times for 5 min each.
15. Dehydrate sections: Incubate sections in 95% ethanol two times for 10 sec each; Repeat in 100% ethanol, incubating sections two times for 10 sec each; Repeat in xylene, incubating sections two times for 10 sec each.
16. Mount sections with coverslips and mounting medium.
|
Biological Description
| Specificity |
|---|
| Elav-type RNA-binding protein ETR3 Antibody [M8J19] detects endogenous levels of total Elav-type RNA-binding protein ETR3 protein. |
| Uniprot ID |
|---|
| O95319 |
| Clone |
|---|
| M8J19 |
| Synonym(s) |
|---|
| BRUNOL3, CUGBP2, ETR3, NAPOR, CELF2, CUGBP Elav-like family member 2, CELF-2, Bruno-like protein 3, CUG triplet repeat RNA-binding protein 2, CUG-BP- and ETR-3-like factor 2, ELAV-type RNA-binding protein 3 |
| Background |
|---|
| Elav-type RNA-binding protein ETR-3 (also known as BRUNOL3, NAPOR, or CUGBP2) is a member of the CELF (CUG-BP and ETR-3-like factor) family of RNA-binding proteins that regulate post-transcriptional gene expression. Structurally, ETR-3 contains three RNA recognition motifs (RRMs)—two near the N-terminus and one at the C-terminus—separated by a divergent central domain (160–230 amino acids) that confers splicing activation potential. ETR-3 is highly expressed in muscle, heart, and brain tissues, where it plays crucial roles in alternative splicing, RNA editing, translation, and mRNA stability. It binds preferentially to UG-rich sequences (UG repeats and UGUU motifs) within pre-mRNAs, regulating exon inclusion or skipping. Through this RNA-binding activity, ETR-3 influences the expression of key genes such as CFTR and MTMR1 and contributes to developmental splicing programs and neuromuscular functions. Dysregulation of ETR-3 and other CELF proteins has been implicated in myotonic dystrophy, where aberrant splicing patterns arise from disrupted CELF and MBNL protein activity. |
| References |
|---|
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.