research use only
Trametinib (GSK1120212) MEK inhibitor
Cat.No.S2673
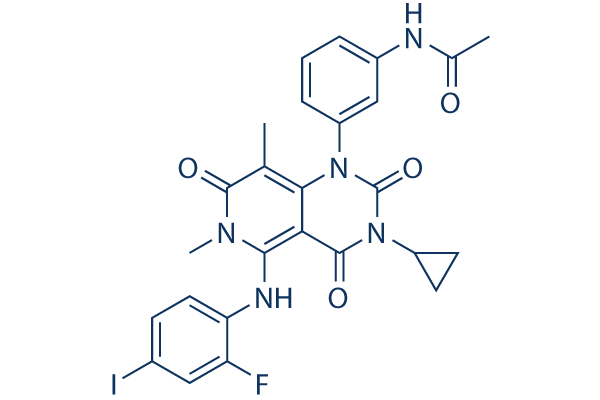
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 615.39
Quality Control
| Related Targets | ERK p38 MAPK Raf JNK Ras KRas S6 Kinase MAP4K TAK1 Mixed Lineage Kinase |
|---|---|
| Other MEK Inhibitors | PD0325901 (Mirdametinib) U0126-EtOH PD98059 PD184352 (CI-1040) BIX 02189 Pimasertib (AS-703026) Refametinib (RDEA119) TAK-733 AZD8330 BIX 02188 |
Cell Culture, Treatment & Working Concentration
| Cell Lines | Assay Type | Concentration | Incubation Time | Formulation | Activity Description | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MDA-MB-231, SW480 and SW1116 cells | Function assay | 100 nM | 24 h | trametinib could decrease YAP levels and inhibit LMB-induced YAP upregulation in MDA-MB-231, SW1116 and SW480 cells | 30833665 | |
| RG7388-resistant U87MG cells | Function assay | 10 nM | 24 h | DMSO | Trametinib treatment reduced the invasive phenotype of RG7388 resistant cells. | 30274984 |
| BJAB cells | Function assay | 0.01μM | 24 h | 0.01 μM trametinib effectively suppressed the ERK hyperactivation in BJAB cells caused by the combined treatment of BKM120 and Danusertib. | 30947576 | |
| Human PDAC cell lines (MIA-PACA, PANC-1, CFPAC-1, PL45, CAPAN-2 and HPAF-II) | Function assay | 10 nM or 100 nM | 3-days or 6-days | The concentration of 10 nM trametinib consistently produced significant differences between gefitinib and trametinib alone compared to combination gefitinib and trametinib in all four sensitive cell lines (CFPAC-1, pl45, CAPAN-2 and HPAF-II). No additive effect was observed in the gefitinib insensitive or excitatory cell lines (MIA-Paca and PANC-1) | 30921351 | |
| Transitional cell carcinoma (TCC) cell lines | Function assay | 25 nM | 6-24 h | Canine TCC cell lines are sensitive to MEK inhibition | 31048548 | |
| COLO205 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.001 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| HT-29 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.001 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| COLO205 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.001 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| MV522 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.001 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| HT-29 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.002 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| MV522 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.002 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| NCI-H727 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.002 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| NCI-H727 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.002 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| SW1417 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.003 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| SW1417 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.003 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| Calu6 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.003 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| LS1034 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.004 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| SW1463 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.004 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| SW1463 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.004 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| Calu6 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.004 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| LS1034 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.005 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| RKO | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.005 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| NCI-H508 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.008 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| KM12 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.01 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| A427 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.01 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| NCI-H1155 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.01 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| HCT8 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.014 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| MDA-MB-175-VII | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.016 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| A549 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.016 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| RKO | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.018 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| NCI-H23 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.02 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| A427 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.022 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| KM12 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.023 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| NCI-H508 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.023 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| MDA-MB-231 | Growth inhibition assay | 3 days | GI50 = 0.025 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| SW837 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.025 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| SW480 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.026 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| NCI-H1355 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.027 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| NCI-H23 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.029 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| EFM19 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.03 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| T84 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.03 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| A549 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.034 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| NCI-H1792 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.035 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| SW480 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.037 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| COR-L23 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.037 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| SW1573 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.038 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| Calu3 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.039 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| HCC827 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.04 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| HOP62 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.05 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| NCI-H1355 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.052 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| NCI-H1792 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.053 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| HCT8 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.055 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| T84 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.061 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| SW900 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.072 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| SW837 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.074 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| DLD1 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.093 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| MDA-MB-175-VII | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.096 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| SW900 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.127 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| Calu3 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.158 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| COR-L23 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.329 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| DLD1 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | IC50 = 0.632 μM | ChEMBL | ||
| Click to View More Cell Line Experimental Data | ||||||
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 8 mg/mL
(12.99 mM)
Water : Insoluble Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 615.39 | Formula | C26H23FIN5O4 |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 871700-17-3 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | JTP-74057 | Smiles | CC1=C2C(=C(N(C1=O)C)NC3=C(C=C(C=C3)I)F)C(=O)N(C(=O)N2C4=CC=CC(=C4)NC(=O)C)C5CC5 | ||
Mechanism of Action
| Features |
More potent than PD0325901 or AZD6244.
|
|---|---|
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
MEK1
(Cell-free assay) 0.92 nM
MEK2
(Cell-free assay) 1.8 nM
|
| In vitro |
Trametinib (GSK1120212) inhibits the phosphorylation of MBP regardless of the isotype of Raf and MEK, with IC50 ranging from 0.92 nM to 3.4 nM. It demonstrates no inhibition of the kinase activities of c-Raf, B-Raf, ERK1 and ERK2. In addition, this compound does not show drastic inhibitory activity against the other 98 kinases. It displays potent inhibitory activity against human colorectal cancer cell lines. HT-29 and COLO205 cells, which are known to have a constitutively active B-Raf mutant, are most sensitive to it with IC50 0.48 nM and 0.52 nM, respectively. The cell lines bearing a K-Ras mutation show a wide range of sensitivity to it with IC50 of 2.2-174 nM. In contrast, COLO320 DM cells, bearing the wild-type gene in both B-Raf and K-Ras, are found to be resistant even at 10 μM. Treatment for 24 hours induces cell-cycle arrest at the G1 phase in all sensitive cell lines. Consistently, it leads to upregulation of p15INK4b and/or p27KIP1 in most of the colorectal cancer cell lines. It inhibits constitutive ERK phosphorylation in all sensitive cell lines. This compound induces apoptosis both in HT-29 and COLO205 cells, but that COLO205 cells are more sensitive than HT-29 cells in terms of apoptosis induction. It blocks tumor necrosis factor-α and interleukin-6 production from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). |
| Kinase Assay |
Raf-MEK-ERK cascade kinase assay
|
|
Non-phosphorylated myelin basic protein (MBP) is coated onto an ELISA plate, and the active form of B-Raf/c-Raf is mixed with unphosphorylated MEK1/MEK2 and ERERK2 in 10 μM ATP and 12.5 mM MgCl2 containing MOPS buffer in the presence of various concentrations of Trametinib (GSK1120212). The phosphorylation of MBP is detected by the anti-phospho-MBP antibody.
|
|
| In vivo |
Oral administration of Trametinib (GSK1120212) at 0.3 mg/kg or 1 mg/kg once daily for 14 days is effective in inhibiting the HT-29 xenograft growth, and 1 mg/kg of this compound almost completely blocks the tumor increase. The phosphorylation of ERK1/2 is completely inhibited in the established tumor tissues by single oral dose of 1 mg/kg, and both p15INK4b and p27KIP1 protein levels are upregulated after 14 days of treatment. In the COLO205 xenograft model, tumor regression is observed even at a dose of 0.3 mg/kg. At a dose of 1 mg/kg, a complete regression is obtained in 4 out of 6 mice in which the tumor degenerates to the point that tumor volume is not measurable. Administration at 0.1 mg/kg almost completely suppresses adjuvant-induced arthritis (AIA) and type II collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) in Lewis rats or DBA1/J mice, respectively. |
References |
|
Applications
| Methods | Biomarkers | Images | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western blot | ERRα / IDH3 / c-Myc / Cyclin D1 pERK /ERK / pS6 / S6 β-catenin |
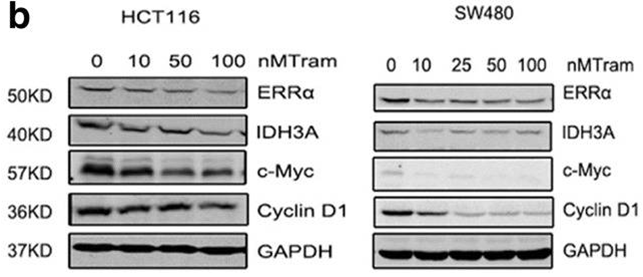
|
30185207 |
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell proliferation MTT assay |
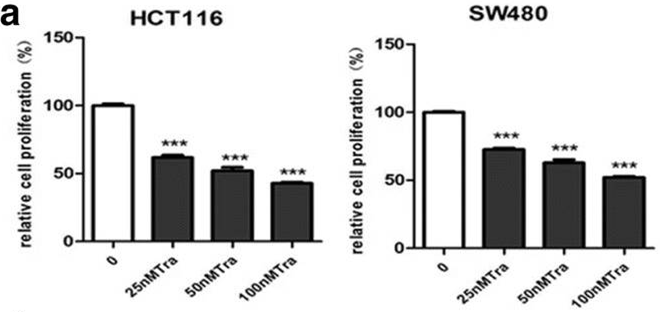
|
30185207 |
| Immunofluorescence | phospho-PR(S345) β-catenin |
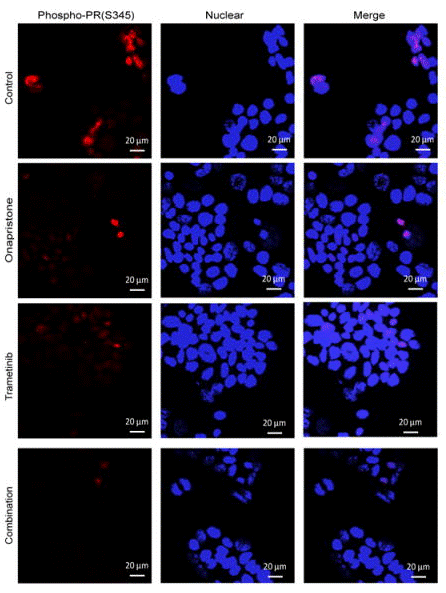
|
29237804 |
Clinical Trial Information
(data from https://clinicaltrials.gov, updated on 2024-05-22)
| NCT Number | Recruitment | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT05275374 | Not yet recruiting | Cancer|BRAF V600 Mutation|Melanoma|Colorectal Cancer|Thyroid Cancer|Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer |
Xynomic Pharmaceuticals Inc. |
December 2024 | Phase 1|Phase 2 |
| NCT06098872 | Not yet recruiting | Arteriovenous Malformations |
University Health Network Toronto |
November 2023 | Phase 2 |
| NCT05907304 | Recruiting | Advanced or Metastatic Solid Tumors |
Erasca Inc. |
August 17 2023 | Phase 1 |
| NCT05874414 | Recruiting | Cholangiocarcinoma |
Genfit |
August 21 2023 | Phase 1|Phase 2 |
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.
Frequently Asked Questions
Question 1:
Could you help us with the best way to prepare it for in vivo i.p. injections?
Answer:
It can be dissolved in 4% DMSO/corn oil at 3 mg/ml clearly.
Question 2:
How to solve the problem that it didn't dissolve up to 10mM in DMSO at room temperature?
Answer:
The solution can be heated up to 50 degrees to help dissolve it. Besides, sonication (with a probe sonicator) also greatly helps with this compound.






































