JNK inhibitors are a class of bioactive molecules that specifically target the c-Jun N-terminal kinases (JNKs), a subfamily of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) involved in regulating a wide range of cellular processes, including cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, and stress responses. In the field of scientific research, the exploration of JNK inhibitors has become a focus due to their potential in intervening in various pathological processes, especially those driven by abnormal MAPK signaling and excessive inflammation.
JNK Inhibitors/Activators
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Information | Product Use Citations | Product Validations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S9614 | CC-90001 | CC-90001 is an orally administered inhibitor of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) with bias for JNK1 over JNK2. It exhibits antifibrotic efficacy and can be used for the research of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. | ||
| S1460 | SP600125 | SP600125 (Nsc75890) is a broad-spectrum JNK inhibitor for JNK1, JNK2 and JNK3 with IC50 of 40 nM, 40 nM and 90 nM in cell-free assays, respectively; 10-fold greater selectivity against MKK4, 25-fold greater selectivity against MKK3, MKK6, PKB, and PKCα, and 100-fold selectivity against ERK2, p38, Chk1, EGFR etc. This compound is also a broad‐spectrum inhibitor of serine/threonine kinases including Aurora kinase A,FLT3 and TRKA with of IC50 of 60 nM, 90 nM and 70 nM. It inhibits autophagy and activates apoptosis. |
|

|
| S4901 | JNK-IN-8 | JNK-IN-8 (JNK Inhibitor XVI) is the first irreversible JNK inhibitor for JNK1, JNK2 and JNK3 with IC50 of 4.7 nM, 18.7 nM and 1 nM, >10-fold selectivity against MNK2, Fms and no inhibition to c-Kit, Met, PDGFRβin A375 cell line. |
|
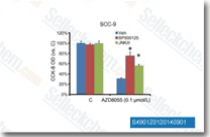
|
| S1950 | Metformin Hydrochloride | Metformin Hydrochloride (1,1-Dimethylbiguanide Hydrochloride) is a highly effective Antihyperglycemic Agent, which primarily decreases hyperglycemia in hepatocytes by suppressing hepatic gluconeogenesis (glucose production by the liver). It also promotes mitophagy in mononuclear cells and induces apoptosis of lung cancer cells through activating the JNK/p38 MAPK pathway and GADD153. |
|
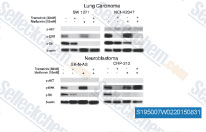
|
| S9698 | Ezatiostat | Ezatiostat, a tripeptide analog of glutathione, is a peptidomimetic inhibitor of Glutathione S-transferase P1-1 (GSTP1-1). This compound activates c-Jun NH2 terminal kinase (JNK1) and ERK1/ERK2 and induces apoptosis. | ||
| S1396 | Resveratrol (trans-Resveratrol) | Resveratrol has a wide spectrum of targets including cyclooxygenases(i.e. COX, IC50=1.1 μM), lipooxygenases(LOX, IC50=2.7 μM), kinases, sirtuins and other proteins. It has anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, blood-sugar-lowering and other beneficial cardiovascular effects. Resveratrol induces mitophagy/autophagy and autophagy-dependent apoptosis. |
|
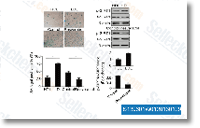
|
| S7409 | Anisomycin (Flagecidin) | Anisomycin (Flagecidin, Wuningmeisu C) is a bacterial antibiotic isolated from Streptomyces griseolus, which inhibits protein synthesis, and also act as a JNK activator. Anisomycin upregulates autophagy and increases apoptosis. |
|

|
| S7508 | JNK Inhibitor IX | JNK inhibitor IX (TCS JNK 5a) is a selective and potent JNK inhibitor with pIC50 of 6.5 and 6.7 for JNK2 and JNK3, respectively. |
|
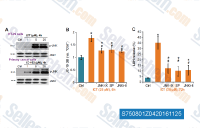
|
| S8490 | Tanzisertib Hydrochloride (CC-930) | Tanzisertib HCl(CC-930, JNK-930, JNKI-1) is kinetically competitive with ATP in the JNK-dependent phosphorylation of the protein substrate c-Jun and potent against all isoforms of JNK (Ki(JNK1) = 44 ± 3 nM, IC50(JNK1) = 61 nM, Ki(JNK2) = 6.2 ± 0.6 nM, IC50(JNK2) = 5 nM, IC50(JNK3) = 5 nM) and selective against MAP kinases ERK1 and p38a with IC50 of 0.48 and 3.4 μM respectively. |
|
|
| S7794 | JNK Inhibitor VIII | JNK Inhibitor VIII (TCS JNK 6o) is an inhibitor of c-Jun N-terminal kinases with IC50 of 45 nM and 160 nM for JNK-1 and JNK-2, respectively. This compound inhibits JNK-1, JNK-2, and JNK-3 with Ki of 2 nM, 4 nM and 52 nM, respectively. |
|
|
Signaling Pathway Map
Core Concepts of JNK Inhibitors and Their Target Biological Molecules
Concepts of JNK Inhibitors: Definition, Classification and Design Principles
The concept of JNK inhibitors is rooted in the specific inhibition of JNK activity to disrupt aberrant signaling transduction pathways. JNKs, also known as stress-activated protein kinases (SAPKs), are serine/threonine kinases that are activated by a variety of extracellular stimuli, such as oxidative stress, cytokines, and DNA damage. JNK inhibitors are designed to bind to JNKs through different mechanisms, including competitive binding to the ATP -binding pocket, allosteric inhibition, or binding to the substrate-binding domain, thereby preventing JNK activation or its interaction with downstream substrates. Based on their chemical properties, JNK inhibitors can be classified into small-molecule inhibitors, peptide inhibitors, and antibody-based inhibitors. Small-molecule inhibitors are the most widely studied due to their advantages of good membrane permeability and easy synthesis. The design principles of JNK inhibitors focus on improving specificity to avoid off-target effects on other kinases (such as p38 MAPK and ERK, which are also members of the MAPK family) and enhancing bioavailability to ensure effective concentration at the target site.
JNK Protein: Structure, Isoforms and Functional Characteristics
The JNK protein family consists of three isoforms encoded by different genes: JNK1 (MAPK8), JNK2 (MAPK9), and JNK3 (MAPK10). JNK1 and JNK2 are widely expressed in various tissues and organs, while JNK3 is mainly expressed in the brain, heart, and testis. The structural characteristics of JNK proteins include a conserved kinase domain, which contains the ATP-binding site and the catalytic site, as well as a regulatory domain that mediates interactions with upstream activators and downstream substrates. The activation of JNK proteins requires dual phosphorylation of threonine and tyrosine residues in the activation loop (Thr183/Tyr185 for JNK1/2/3) by upstream MAPK kinases (MKK4 and MKK7). Different JNK isoforms exhibit functional redundancy in some cellular processes but also have specific roles. For example, JNK1 and JNK2 are involved in the regulation of inflammatory responses and cell proliferation, while JNK3 is closely associated with neuronal apoptosis and neurodegenerative diseases. The structural and functional differences among JNK isoforms provide important targets for the development of isoform-specific JNK inhibitors.
The Role of JNK Inhibitors in MAPK Pathway Regulation
MAPK Pathway: Composition and JNK-Mediated Signaling Cascade
The MAPK pathway is a highly conserved signaling pathway in eukaryotes that transmits extracellular signals to the nucleus to regulate gene expression. The classic MAPK pathway consists of a three-tier kinase cascade: MAPK kinase kinases (MAP3Ks), MAPK kinases (MAP2Ks), and MAPKs. In the JNK-mediated MAPK pathway, upstream stimuli activate MAP3Ks (such as ASK 1, MEKK1-4), which in turn phosphorylate and activate MAP2Ks (MKK4 and MKK7). Activated MKK4 and MKK7 then phosphorylate and activate JNKs. Activated JNKs translocate from the cytoplasm to the nucleus, where they phosphorylate downstream transcription factors, such as c-Jun, ATF2, and Elk-1. These phosphorylated transcription factors form dimers and bind to specific DNA response elements (such as AP-1) to regulate the expression of target genes involved in inflammation, apoptosis, and cell cycle progression. The JNK-mediated MAPK pathway is tightly regulated under physiological conditions, but its aberrant activation is closely related to the pathogenesis of many diseases, such as inflammatory bowel disease, rheumatoid arthritis, and cancer.
Mechanisms of JNK Inhibitors in Regulating MAPK Pathway and Gene Expression
JNK inhibitors exert their regulatory effects on the MAPK pathway by blocking the activation of JNKs or their downstream signaling events. Small-molecule JNK inhibitors that target the ATP-binding pocket compete with ATP for binding to JNKs, thereby inhibiting the phosphorylation of JNKs by upstream MKKs or the phosphorylation of downstream substrates by JNKs. Allosteric JNK inhibitors bind to a site outside the ATP-binding pocket, inducing conformational changes in JNKs that prevent their activation or interaction with substrates. By inhibiting JNK activity, JNK inhibitors can downregulate the expression of downstream target genes. For example, in inflammatory responses, activated JNKs promote the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines (such as TNF-α, IL -6, and IL-1β) by phosphorylating c-Jun and activating the AP-1 transcription factor. JNK inhibitors can inhibit the production of these pro-inflammatory cytokines by blocking JNK-mediated AP-1 activation. In addition, JNK inhibitors can also regulate the expression of genes involved in cell apoptosis, such as Bcl-2 family members, by inhibiting JNK signaling, thereby exerting anti-apoptotic effects in certain pathological conditions.
Research Progress of JNK Inhibitors in Inflammatory Diseases
The Role of JNK Kinase in Inflammatory Responses
Inflammatory response is a complex physiological and pathological process that is initiated by the recognition of pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) or damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) by immune cells. JNK kinase plays a key role in the regulation of inflammatory responses. When immune cells are stimulated by PAMPs or DAMPs, the JNK-mediated MAPK pathway is rapidly activated, which promotes the production and release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, chemokines, and inflammatory mediators (such as nitric oxide and prostaglandins). These inflammatory factors further recruit immune cells to the site of inflammation, amplifying the inflammatory response. Abnormal activation of JNK kinase can lead to excessive inflammatory responses, which are involved in the pathogenesis of various chronic inflammatory diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, and inflammatory bowel disease. For example, in rheumatoid arthritis, the synovial tissue of patients shows high levels of JNK activation, and the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines (such as TNF-α and IL-6) mediated by JNK signaling promotes synovial hyperplasia, cartilage destruction, and bone erosion.
Preclinical and Clinical Research of JNK Inhibitors in Inflammatory Diseases
Due to the important role of JNK kinase in inflammatory responses, JNK inhibitors have become potential therapeutic agents for inflammatory diseases, and a large number of preclinical and clinical studies have been carried out. In preclinical studies, various JNK inhibitors have been shown to exert anti-inflammatory effects in animal models of inflammatory diseases. For example, in a mouse model of collagen-induced arthritis (CIA), administration of JNK inhibitors can significantly reduce the severity of arthritis, inhibit synovial hyperplasia and bone destruction, and reduce the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines in serum and synovial tissue. In a mouse model of dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis, JNK inhibitors can alleviate intestinal inflammation, reduce intestinal mucosal damage, and improve the survival rate of mice. In clinical studies, some JNK inhibitors have entered phase I and phase II clinical trials for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. For example, AS601245, a small-molecule JNK inhibitor, has been tested in clinical trials for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, and the results show that it can reduce the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines in patients and improve clinical symptoms. However, some JNK inhibitors have shown certain side effects in clinical trials, such as liver toxicity and hematological abnormalities, which limit their clinical application. Therefore, the development of isoform-specific JNK inhibitors with higher specificity and lower toxicity is the focus of current research.
In conclusion, JNK inhibitors, as important regulators of the MAPK pathway, have important scientific research value and broad therapeutic prospects in the field of inflammatory diseases. In-depth exploration of the concepts, mechanisms of action, and interaction with JNK proteins, kinases, and downstream genes of JNK inhibitors will help to optimize the design of JNK inhibitors and improve their therapeutic efficacy and safety. With the continuous progress of research, it is expected that JNK inhibitors will become a new class of therapeutic drugs for the treatment of inflammatory diseases and other diseases related to abnormal JNK signaling.





































