research use only
Phenibut GABA Receptor agonist
Cat.No.S4892
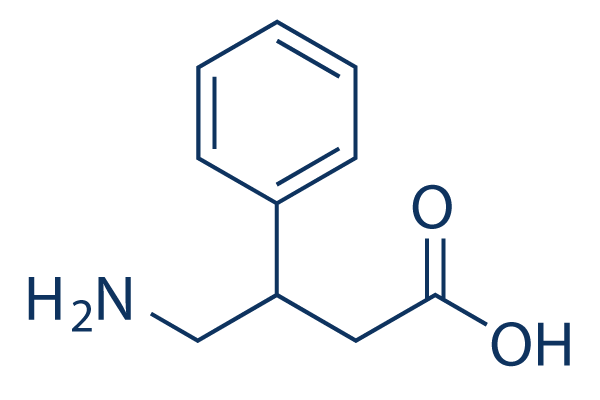
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 179.22
Quality Control
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 36 mg/mL
(200.87 mM)
Water : 36 mg/mL Ethanol : 36 mg/mL |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 179.22 | Formula | C10H13NO2 |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 1078-21-3 | -- | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | Aminophenylbutyric acid, Fenibut, Fenigam, Phenigam, Phenybut, PhGABA, β-Phenyl-γ-aminobutyric acid, β-Phenyl-GABA | Smiles | C1=CC=C(C=C1)C(CC(=O)O)CN | ||
Mechanism of Action
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
GABA receptor
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Phenibut has anxiolytic and nootropic (cognition enhancing) effects. It acts as a GABA-mimetic, primarily at GABAB and, to some extent, at GABAA receptors. This compound also stimulates dopamine receptors and antagonizes β-phenethylamine (PEA), a putative endogenous anxiogenic. |
| In vivo |
At doses that do not affect motor activity (e.g., 20 mg/kg i.p.), Phenibut inhibits food conditioned reflexes in mice. At doses higher than 70 mg/kg i.p., this compound reduces motor and exploratory activities, rearings, muscle tone, coordination and body temperature. Following intravenous administration to either rabbits or rats it is not metabolized. This chemical is largely excreted in the urine. At 15, 30, 60, or 90 min following i.v. administration it is found in liver, kidneys, and urine. Traces of the compound are found in blood and brain. 180 min after i.v. injection only traces of the drug are found in all tissues studied. In cats and dogs, it, after a single dose of 50 mg/kg i.v., is excreted in the urine unchanged. The acute toxicity of this substance is low. Its LD50 is 900 mg/kg i.p. in mice and 700 mg/kg i.p. in rats. Administration of this agent leads to decreases in horizontal movement activity and some elements of investigative behavior in rabbits in the open field, along with decreases in the reactivity of the animals to emotionally significant stimuli. |
References |
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































