research use only
Acemetacin COX inhibitor
Cat.No.S2602
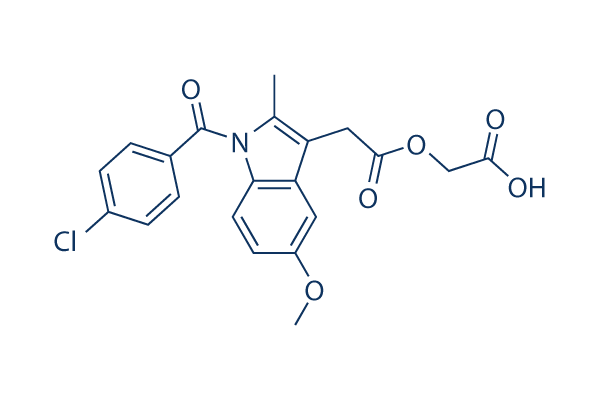
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 415.82
Quality Control
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 83 mg/mL
(199.6 mM)
Ethanol : 83 mg/mL Water : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 415.82 | Formula | C21H18ClNO6 |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 53164-05-9 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | K-708,TVX 1322 | Smiles | CC1=C(C2=C(N1C(=O)C3=CC=C(C=C3)Cl)C=CC(=C2)OC)CC(=O)OCC(=O)O | ||
Mechanism of Action
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
COX
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Acemetacin is less potent than indomethacin in causing a concentration-related inhibition of PGE accumulation in gastric mucosal incubates. This compound is also less potent than indomethacin in reducing gastric 6-keto-PGF1 alpha and TXB2. It probably exerts actions independent of conversion to Indomethacin, given the different effects of these two drugs on LTB(4) production. This prodrug of indomethacin exhibits better gastric tolerability in preclinical and clinical trials. It involves the sequential participation of nitric oxide (NO) or K+ channel pathways to confer its antinociceptive effect. This compound exhibits the anti-inflammatory effect through PG synthesis inhibition. It prevents the PGE2 release only at the high concentration of 10 μM in inflamed synovial tissue. This chemical exhibits less potent inhibitory effect on PGE2 release from the synovial membrane in the in vitro study. |
| In vivo |
This compound induces significantly less gastric and intestinal damage than indomethacin in rats pretreated with inhibitors of COX-2 and NOS, despite markedly suppressing COX activity. |
References |
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































