- Inhibitors
- Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
Daidzin Dehydrogenase inhibitor
Cat.No.S2289
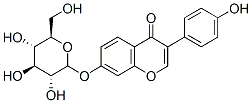
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 416.38
Jump to
Quality Control
Batch:
Purity:
99.96%
99.96
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 83 mg/mL
(199.33 mM)
Water : Insoluble Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
Dilution Calculator
Molecular Weight Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
mg/kg
g
μL
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
%
DMSO
%
%
Tween 80
%
ddH2O
%
DMSO
+
%
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 416.38 | Formula | C21H20O9 |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 552-66-9 | -- | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | Daidzoside, Daidzein 7-O-glucoside, Daidzein 7-glucoside | Smiles | C1=CC(=CC=C1C2=COC3=C(C2=O)C=CC(=C3)OC4C(C(C(C(O4)CO)O)O)O)O | ||
Mechanism of Action
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
ALDH-Ⅰ
(Cell-free assay) 20 nM(Ki)
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Daidzin, a glycoside of daidzein, increases the transcriptional activity of RARα and RARγ but does not bind to the RARs. This compound does not inhibit human class Ⅰ, Ⅱ, or Ⅲ alcohol dehydrogenases, nor does it have any significant effect on biological systems that are known to be affected by other isoflavones. It inhibits human ALDH-I and ALDH-II in a concentration-dependent manner. This chemical inhibits both ALDH-I and ALDH-II in an apparently competitive manner with Ki values of 40 nM and 20 μM, respectively, and it inhibits ALDH-I uncompetitively with respect to NAD+. The inhibition of ALDH-I by daidzin is reversible.
|
| In vivo |
Daidzin has no effect on alcohol-metabolizing enzymes(i.e., ADH and ALDH) when given to rats intragastrically. Chronic administration of this compound exerts an effect on alcohol pharmacokinetics, although the effect is less pronounced than when it is administered concurrently with ethanol.It is shown to shorten sleep time if ethanol is given intragastrically, but not when given intraperitoneally, indicating absence of effect on ethanol elimination rate. This chemical delays ethanol absorption and lessens alcohol intoxication. It is shown to suppress the levels of BAC(blood alcohol concentration) for the first 3 hr after alcohol ingestion in both fasted and fed rats. These effects may in part be due to its antioxidant activity.
|
References |
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































