research use only
Galanthamine AChR inhibitor
Cat.No.S3866
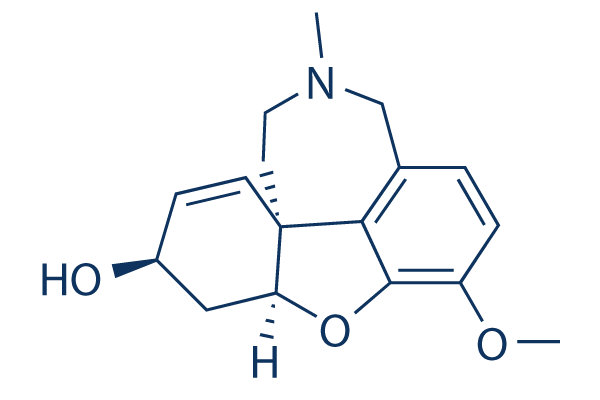
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 287.35
Quality Control
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 40 mg/mL
(139.2 mM)
Water : 20 mg/mL Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 287.35 | Formula | C17H21NO3 |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 357-70-0 | -- | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
Mechanism of Action
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
AChE
(Cell-free assay) 0.35 μM
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Galantamine shows reversible, competitive acetylcholinesterase inhibiting and nicotinic acetylcholinergic receptor modulatory properties. Galantamine reduced the release of reactive oxygen species (up to 50%) and prevented loss in mitochondrial activity. Galantamine treatment resulted in a significant inhibition of H2O2-induced nitrite generation. Galantamine also concentration-dependently inhibited AChE activity (28–88%) in H2O2–SK-N-SH cells after 24 h. This drug, which facilitates cholinergic neurotransmission, is also neuroprotective by lowering oxidative injury.
|
| In vivo |
Generally, oral absorption was rapid, with maximal plasma levels reached within 2 h in all species. Absolute oral bioavailability of a gavage dose was high in rat (77 %) and dog (78 %). In mice and rats, the bioavailability of galantamine administered via the food was lower than of galantamine administered by gavage. Elimination half-life of galantamine was relatively large in rat and dog and smaller in mouse and rabbit. After i.v. administration, galantamine plasma levels declined fairly rapidly in the various animal species tested with an elimination half-life of 1−5 h in the rat and 4−7 h in the dog. The volume of distribution was 4−5 l/kg in rats and dogs. Plasma clearance was highest in male rats, 1.9 l/kg/h, about twice the value of female rats and of dogs. Sex differences in pharmacokinetics of galantamine were shown to exist in rats and mice. Male rats generally had lower plasma values of galantamine and lower exposure rates; in mice, the effect was opposite. In dogs, no sex differences in the pharmacokinetics of galantamine could be detected. In mice and rats, the bioavailability of galantamine administered via the food was lower than of galantamine administered by gavage.
|
References |
|
Clinical Trial Information
(data from https://clinicaltrials.gov, updated on 2024-05-22)
| NCT Number | Recruitment | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT00299676 | Completed | Alzheimer Disease|Dementia|Galantamine |
Janssen-Cilag Pty Ltd |
May 2005 | -- |
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































