research use only
TBHQ Nrf2 activator
Cat.No.S4990
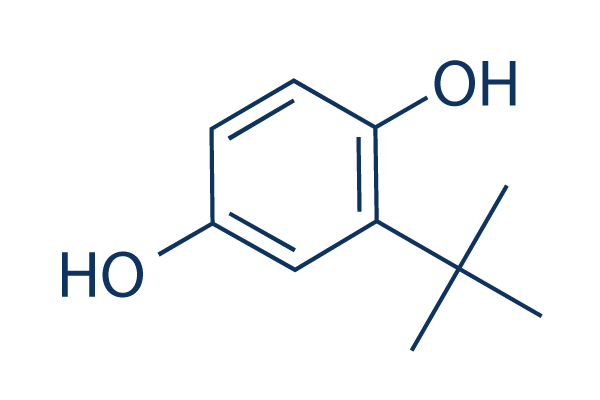
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 166.22
Quality Control
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 33 mg/mL
(198.53 mM)
Ethanol : 33 mg/mL Water : 4 mg/mL |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 166.22 | Formula | C10H14O2 |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 1948-33-0 | -- | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | Tert-butylhydroquinone | Smiles | CC(C)(C)C1=C(C=CC(=C1)O)O | ||
Mechanism of Action
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
Nrf2
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Tert-butylhydroquinone (tBHQ) is a metabolite of the chemical compound butylated hydroxyanisole and induces Nrf2 activation and conveys protection against hydrogen peroxide, 6-hydroxydopamine, the pesticidal deltamethrin, and other toxicants. This compound preferentially alters the redox status in the mitochondrial compartment in HeLa cells. HeLa cells treated with this chemical show a preferential oxidation of mitochondrial thioredoxin-2 (Trx2), while cellular glutathione and cytosolic thioredoxin-1 are not affected. In cultured H9c2 cells and primary cardiac myocytes, it stimulates Akt phosphorylation and suppresses oxidant-induced apoptosis.
|
| In vivo |
TBHQ treatment elicits significant cytoprotective actions in different organs under pathological conditions. Systemic or local intra-cerebroventricular treatment with this compound in an ischemic stroke model in rats significantly reduces the infarct size and neurological deficits. Administration of this chemical in rats suppresses renal damage and oxidative stress after ischemia and reperfusion injury. In mice with type 1 diabetes, chronic treatment with this compound significantly reduces the degree of glomerular fibrosis and ameliorates proteinuria. This compound prevents left ventricular dilatation and cardiac dysfunction induced by transverse aortic constriction (TAC), and decreases the prevalence of myocardial apoptosis. The beneficial effects of this chemical are associated with an increase in Akt activation, but not related to activations of Nrf2 or AMP-activated protein kinase. This compound-induced Akt activation is accompanied by increased phosphorylation of Bad, glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β) and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR).
|
References |
|
Applications
| Methods | Biomarkers | Images | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
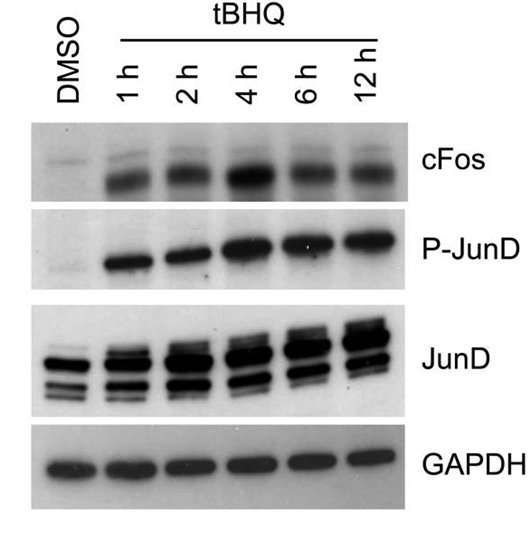
| Western blot | c-Fos / p-JunD / JunD p-JNK / JNK / p-ERK / ERK p-AKT / AKT α-Nrf2 / α-AKR1C1 |
|
24830941 |
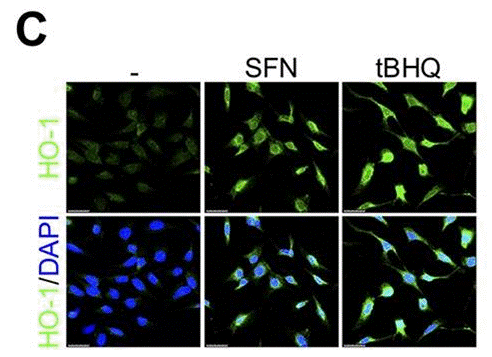
| Immunofluorescence | HO-1 |
|
31333462 |
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































