research use only
Triclabendazole Microtubule Associated inhibitor
Cat.No.S4114
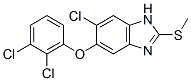
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 359.66
Quality Control
| Related Targets | Akt Wnt/beta-catenin PKC HSP ROCK Integrin Bcr-Abl Actin FAK Kinesin |
|---|---|
| Other Microtubule Associated Inhibitors | Nocodazole MMAF Patupilone (Epothilone B) CW069 Lexibulin (CYT997) Combretastatin A4 Epothilone A ABT-751 (E7010) Cucurbitacin B TAI-1 |
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 72 mg/mL
(200.18 mM)
Ethanol : 36 mg/mL Water : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 359.66 | Formula | C14 H9Cl3N2OS |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 68786-66-3 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | CGA-89317,tcbz | Smiles | CSC1=NC2=CC(=C(C=C2N1)Cl)OC3=C(C(=CC=C3)Cl)Cl | ||
Mechanism of Action
| Features |
Rapidly removed by the liver and oxidized to the sulphoxide and sulphone metabolites.
|
|---|---|
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
Tubulin
|
| In vitro |
Triclabendazole treatment produces percentage decreases of the fluke egg output by 15.3%, 4.3% and 36.6%, respectively, in sheep, dairy cows and heifers, these results indicate the presence of TCBZ-resistant Fasciola hepatica in sheep and cattle on this farm. This compound sulphoxide (50 mg/mL) results in extensive damage to the tegument of triclabendazole-susceptible F. hepatica, whereas triclabendazole-resistant flukes shows only localized and relatively minor disruption of the tegument covering the spines. |
| In vivo |
Triclabendazole is metabolized into a number of compounds, depending on the route of administration, plasma levels peak at 18-24 hours (this compound sulphoxide) and 36-48 hours (this compound sulphone), neither this compound nor any other metabolites can be detected in plasma. This compound sulphoxide blocks the transport of secretory bodies from the cell body to the tegumental surface, the block occurs at the site of their formation by the Golgi complex in the cell body, in their movement through the cytoplasmic connections to the syncytium, and in their movement from the base to the apex of the syncytium. This chemical binds to the colchicine binding site on the β-tubulin molecule and this has been used at the basis for evaluating the relative acitvity of this chemical. It is administered intraruminally at 10 mg/kg to sheep, this chemical metabolites present in plasma are only TCBZ sulphoxide (TCBZ-SO) and TCBZ sulphone, their maximum concentrations (greater than 13 mg/mL) at 18 hours and 36 hours, respectively. This compound metabolites are specifically bound to plasma albumin, which is believed to exert a major influence on the duration of plasma TCBZ metabolite concentrations and consequent exposure of liver fluke. This chemical (40 mg/kg) kills 99% of adult flukes in the rat. |
References |
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































