research use only
Sinapinic Acid HDAC inhibitor
Cat.No.S3981
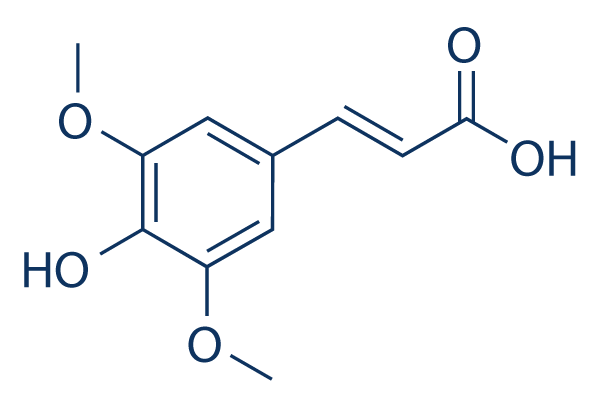
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 224.21
Quality Control
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 44 mg/mL
(196.24 mM)
Ethanol : 44 mg/mL Water : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 224.21 | Formula | C11H12O5 |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 530-59-6 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | Sinapic acid | Smiles | COC1=CC(=CC(=C1O)OC)C=CC(=O)O | ||
Mechanism of Action
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
HDAC
ACE1
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Sinapic acid is widespread in the plant kingdom (fruits, vegetables, cereal grains, oilseed crops, and some spices and medicinal plants). Sinapic acid shows antioxidant, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, and anti-anxiety activity. Sinapic acid inhibits nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) activation in macrophages. Via NF-κB inactivation sinapic acid suppresses the expression of proinflammatory mediators such as inducible nitric oxide synthase, cyclooxygenase-2, tumor necrosis factor-α, and interleukin-1β. Sinapic acid exerts an inhibitory effect against tumorigenic colon cells, but a low influence on breast cancer cells. It also shows antiproliferative action (ability to prevent, or retard, the spread of malignant cells into surrounding tissue) on the human breast cancer T47D cell line. |
| In vivo |
Sinapic acid is an important anxiolytic (anti-anxiety) agent. Its anxiolytic-like effect is mediated by the γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) neurotransmitter system. Sinapic acid might act like the agonist of a specific GABA receptor. Due to its metal-chelating ability, it has a protective effect against arsenic-induced toxicity in rats as measured by the activities of serum hepatospecific enzymes, together with lipid peroxidative markers. SA inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced NO, prostaglandin E2, tumor necrosis factor-α and interleukin-1β production in a dose-dependent manner through the suppression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), cyclooxygenase-2, and proinflammatory cytokines expressions. In addition, SA exhibits cognitive-ameliorating effects in a CO2- or scopolamine-induced mouse amnesic model. It attenuates Aβ1-42 protein-induced hippocampal neuronal cell death and thus exhibits neuroprotection against Aβ protein-induced neuronal injuries. |
References |
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































