research use only
Pheniramine Maleate Histamine Receptor antagonist
Cat.No.S4045
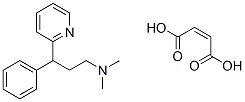
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 356.42
Quality Control
| Related Targets | Adrenergic Receptor AChR 5-HT Receptor COX Calcium Channel Dopamine Receptor GABA Receptor TRP Channel Cholinesterase (ChE) GluR |
|---|---|
| Other Histamine Receptor Inhibitors | GSK2879552 Dihydrochloride JNJ-7777120 Ebastine Mianserin HCl Astemizole Ciproxifan Maleate Lafutidine Mizolastine Dimethindene maleate Rupatadine |
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 71 mg/mL
(199.2 mM)
Water : 71 mg/mL Ethanol : 71 mg/mL |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 356.42 | Formula | C16H20N2.C4H4O4 |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 132-20-7 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | N/A | Smiles | CN(C)CCC(C1=CC=CC=C1)C2=CC=CC=N2.C(=CC(=O)O)C(=O)O | ||
Mechanism of Action
| In vitro |
Pheniramine Maleate is a histamine H1 antagonists with little sedative action. It is used in treatment of hay fever, rhinitis, allergic dermatoses, and pruritus. Pheniramine appears to compete with histamine for histamine H1- receptor sites on effector cells. The antihistamines antagonize those pharmacological effects of histamine which are mediated through activation of H1- receptor sites and thereby reduce the intensity of allergic reactions and tissue injury response involving histamine release. Antihistamines suppress the histamine-induced wheal (swelling) and flare (vasodilation) response by blocking the binding of histamine to its receptors on nerves, vascular smooth muscle, glandular cells, endothelium, and mast cells. They effectively exert competitive antagonism of histamine for H1-receptors.
|
References |
|---|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































