research use only
Oxyresveratrol Tyrosinase inhibitor
Cat.No.S4739
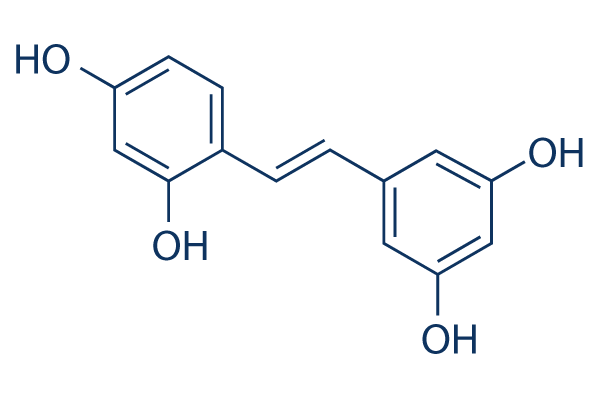
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 244.24
Quality Control
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 49 mg/mL
(200.62 mM)
Ethanol : 49 mg/mL Water : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 244.24 | Formula | C14H12O4 |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 29700-22-9 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | Tetrahydroxystilbene, 2,3',4,5'-tetrahydroxystilbene | Smiles | C1=CC(=C(C=C1O)O)C=CC2=CC(=CC(=C2)O)O | ||
Mechanism of Action
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
tyrosinase
DPPH
28.9 μM
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Oxyresveratrol has been reported to inhibit β-amyloid-induced neurotoxicity in cultured cortical neurons and in vitro activity of β-secretase, an enzyme vital for the production of the Aβ protein. And it can also prevent neurotoxicity and DNA damage through its antioxidant properties in cultured neuronal cells. This compound shows modest inhibitory activity against H5N1 neuraminidase (an enzyme found in avian influenza virus), but strong inhibition against α-glucosidase, an enzyme responsible for the breaking down of starch and polysaccharides into glucose in the intestine. It is an effective radical scavenger. This chemical protects hepatocytes against oxidative stress, mitochondrial damage, and resultant cell death. It induces activation of an antioxidant transcription factor, Nrf2, mediated through ERK phosphorylation.
|
| In vivo |
Oxyresveratrol has been reported to undergo extensive hepatic metabolism and rapid urinary elimination, resulting in a short half-life time, and thereby restricting its clinical use. Moreover, its postulated function as a preventive agent for neurodegenerative disorders, such as AD or PD, appears to be hindered by its low ability to cross the blood-brain barrier (BBB). Despite its moderate in vitro inhibitory activity against herpes simplex virus type I (HSV-1), this compound, in the form of topical cream, exhibits high therapeutic efficacy in mice cutaneously infected with HSV-1, with a potency comparable to that of the antiviral drug acyclovir. It ameliorates acute liver injury caused by CCl4 in mice.
|
References |
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































