research use only
MLN2238 (Ixazomib) Proteasome inhibitor
Cat.No.S2180
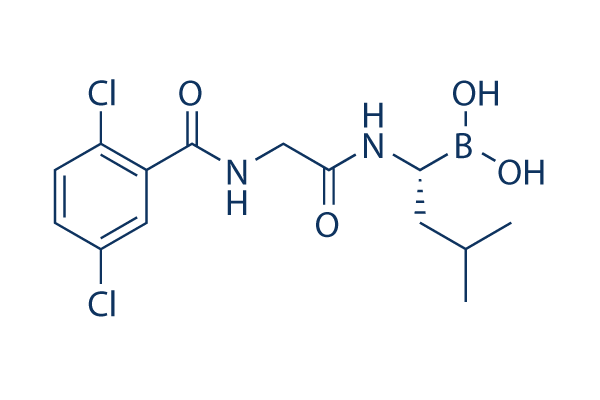
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 361.03
Quality Control
| Related Targets | HDAC Caspase Secretase MMP HCV Protease Cysteine Protease Tyrosinase DPP HIV Protease Serine Protease |
|---|---|
| Other Proteasome Inhibitors | MG132 Celastrol Epoxomicin (BU-4061T) ONX-0914 (PR-957) Oprozomib Delanzomib VR23 Marizomib (Salinosporamide A) PI-1840 KSQ-4279 (USP1-IN-1) |
Cell Culture, Treatment & Working Concentration
| Cell Lines | Assay Type | Concentration | Incubation Time | Formulation | Activity Description | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HEK293 | Function assay | 1 hr | Inhibition of NFkappaB in HEK293 cells incubated for 1 hr prior to TNF-alpha challenge measured after 3 hrs by luciferase reporter gene assay relative to control, IC50 = 0.0062 μM. | ChEMBL | ||
| Calu6 | Function assay | 1 hr | Inhibition of 26S proteasome beta5 subunit in human Calu6 cells using Suc-LLVY-aminoluciferin as substrate after 1hr by luminescence assay, IC50 = 0.009 μM. | ChEMBL | ||
| Calu6 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human Calu6 cells after 72 hrs by luminescence assay, LC50 = 0.014 μM. | ChEMBL | ||
| U266B1 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human U266B1 cells assessed as reduction in cell viability after 72 hrs by CellTiter 96 aqueous one solution assay, IC50 = 0.05215 μM. | 29934218 | ||
| RPMI8226 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human RPMI8226 cells assessed as reduction in cell viability after 72 hrs by CellTiter 96 aqueous one solution assay, IC50 = 0.05532 μM. | 29934218 | ||
| ARH77 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human ARH77 cells assessed as reduction in cell viability after 72 hrs by CellTiter 96 aqueous one solution assay, IC50 = 0.0655 μM. | 29934218 | ||
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| U-2 OS | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for U-2 OS cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for A673 cells | 29435139 | |||
| DAOY | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for DAOY cells | 29435139 | |||
| Saos-2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-37 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-37 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-12 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-12 cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-12 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for BT-12 cells | 29435139 | |||
| DAOY | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for DAOY cells | 29435139 | |||
| fibroblast cells | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for control Hh wild type fibroblast cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh41 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh41 cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for A673 cells) | 29435139 | |||
| Rh30 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh30 cells | 29435139 | |||
| U-2 OS | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for U-2 OS cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh41 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for Rh41 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB-EBc1 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB-EBc1 cells | 29435139 | |||
| LAN-5 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh18 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh18 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh18 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for Rh18 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Click to View More Cell Line Experimental Data | ||||||
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 72 mg/mL
(199.42 mM)
Ethanol : 72 mg/mL Water : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 361.03 | Formula | C14H19BCl2N2O4 |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 1072833-77-2 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | N/A | Smiles | B(C(CC(C)C)NC(=O)CNC(=O)C1=C(C=CC(=C1)Cl)Cl)(O)O | ||
Mechanism of Action
| Features |
A first-in-class proteasome inhibitor that has improved pharmacokinetics (PK), pharmacodynamics(PD), and antitumor activity in preclinical studies.
|
|---|---|
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
20S proteasome
(Cell-free assay) 0.93 nM(Ki)
20S proteasome
(Cell-free assay) 3.4 nM
|
| In vitro |
At higher concentrations, this compound also inhibits the caspase-like (β1) and trypsin-like (β2) proteolytic sites with IC50 of 31nM and 3.5uM, respectively. It inhibits Calu-6 cell with IC50 of 9.7 nM. MLN2238 is a selective, potent, and reversible inhibitor of the proteasome in tumor cells. This compound shows time-dependent reversible proteasome inhibition. Both this compound and Bortezomib shows time-dependent reversible proteasome inhibition; however, the proteasome dissociation half-life for it is determined to be ∼6-fold faster than that of Bortezomib (18 and 110 minutes, respectively). It dissociates more rapidly from the proteasome than Bortezomib, consistent with faster recovery of proteasome activity observed in the Proteasome-Glo assay. It has a greater overall tumor pharmacodynamic effect than Bortezomib as assessed by 20S inhibition. This compound is the biologically active form of MLN9708.
|
| Kinase Assay |
Kinase assay
|
|
Calu-6 cells are cultured in MEM containing 10% fetal bovine serum and 1% penicillin/streptomycin and plated 1 day before the start of the experiment at 1 × 104 cells per well in a 384-well plate. Proteasome activity is assessed by monitoring hydrolysis of the chymotrypsin-like substrate Suc-LLVY-aminoluciferin in the presence of luciferase using the Proteasome-Glo assay reagents according to the manufacturer's instructions. Luminescence is measured using a LEADseeker instrument.
|
|
| In vivo |
MLN2238 induces a greater pharmacodynamic response than Bortezomib in xenograft tumors. This compound shows greater maximum and sustained tumor proteasome inhibition compared with Bortezomib in xenograft models. These results confirm that the improved tumor exposure seen with this agent translates into an improved tumor pharmacodynamic response both at the level of and downstream from the proteasome. It shows antitumor activity in the CWR22 xenograft model. This chemical shows greater tumor pharmacodynamic responses in WSU-DLCL2 xenografts compared with Bortezomib. Similarly, Bortezomib treatment only led to a minor increase in GADD34 levels in WSU-DLCL2 xenograft tumors, whereas it strongly induces its expression. This compound has an improved pharmacodynamic profile and antitumor activity compared with Bortezomib in both OCI-Ly10 and PHTX22L models.
|
References |
|
Applications
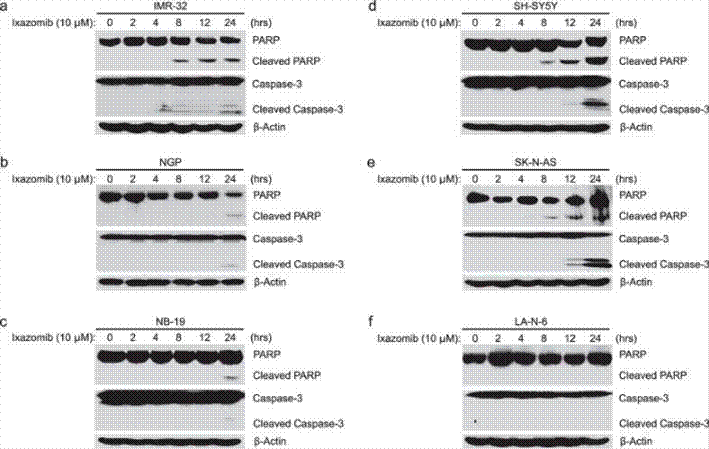
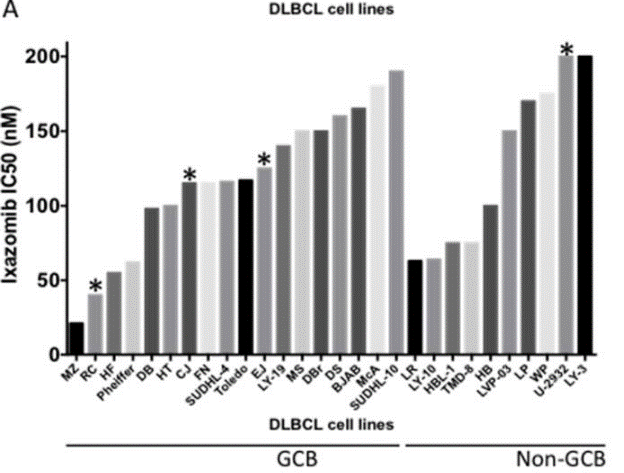
| Methods | Biomarkers | Images | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western blot | PARP / Cleaved PARP / Caspase-3 / Cleaved Caspase-3 Mcl-1 / Bcl-2 p53 / p21 / NOXA / PUMA / pRb / E2F / Cyclin D1 / CDK6 |
|
27687684 |
| Growth inhibition assay | IC50 |
|
29416618 |
Clinical Trial Information
(data from https://clinicaltrials.gov, updated on 2024-05-22)
| NCT Number | Recruitment | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT00963820 | Completed | Multiple Myeloma |
Millennium Pharmaceuticals Inc.|Takeda |
October 2009 | Phase 1 |
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































