research use only
Gabapentin HCl GABA Receptor agonist
Cat.No.S1338
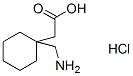
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 207.7
Quality Control
Solubility
|
In vitro |
Water : 42 mg/mL
DMSO
: Insoluble
Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 207.7 | Formula | C9H17NO2.HCl |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 60142-95-2 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | Neurontin HCl | Smiles | C1CCC(CC1)(CC(=O)O)CN.Cl | ||
Mechanism of Action
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
GABA receptor
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Gabapentin suppresses ectopic afferent discharge activity generated from injured peripheral nerves. Gabapentin, in a range of 30 to 90 mg/kg, significantly attenuates allodynia in nerve-injured rats. Gabapentin dose-dependently inhibits the ectopic discharge activity of 15 injured sciatic afferent nerve fibers through an action on impulse generation. Gabapentin inhibits KCl (30 mM)-evoked voltage-dependent Ca(2+) influx. Gabapentin potently inhibits the peak whole-cell Ca(2+) channel current (I(Ba)) in a dose-dependent manner with an estimated IC(50) value of 167 nM. Gabapentin inhibition is voltage-dependent, producing an approximately 7 mV hyperpolarizing shift in current voltage properties and reducing a non-inactivating component of whole-cell current activated at relatively depolarized potentials. Gabapentin selectively activates heterodimeric GABAB1a-B2 receptors, but not GABAB1b-B2 or GABAB1c-B2 receptors. Gabapentin selectively activates presynaptic GABAB heteroreceptors on glutamatergic terminals, but not GABAB autoreceptors on GABAergic terminals. Gabapentin is found to inhibit both the excitatory synaptic transmission in vitro and the neuronal response to noxious electrical and mechanical stimulation in vivo mediated by α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA), but not those mediated by N-methyl-D-asparate (NMDA) receptors. Gabapentin acts as an AMPA-receptor antagonist in the rat spinal cord to exert its spinal antinociceptive effect. Gabapentin depresses, but NMDA enhanced, the presynaptic fiber volley in the CA1 region of rat hippocampal slices. |
References |
|
Clinical Trial Information
(data from https://clinicaltrials.gov, updated on 2024-05-22)
| NCT Number | Recruitment | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT04613024 | Not yet recruiting | Weight Loss|Pain Postoperative |
Stanford University |
July 1 2023 | Early Phase 1 |
| NCT05276089 | Not yet recruiting | Opioid Use |
Dr Yu Fu|Teesside University|NIHR Applied Research Collaboration for North East and North Cumbria|North East Academic Health Science Network|Newcastle University |
February 1 2023 | Not Applicable |
| NCT05609682 | Recruiting | Post Operative Pain |
University of Oklahoma |
November 29 2022 | Early Phase 1 |
| NCT05750875 | Completed | Pruritus|Uremia|Chronic Kidney Diseases |
King Edward Medical University |
May 1 2022 | Phase 4 |
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































