research use only
D-glutamine GluR chemical
Cat.No.S1893
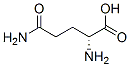
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 146.14
Quality Control
Solubility
|
In vitro |
Water : 9 mg/mL
DMSO
: Insoluble
Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 146.14 | Formula | C5H10N2O3 |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 5959-95-5 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | N/A | Smiles | C(CC(=O)N)C(C(=O)O)N | ||
Mechanism of Action
| In vitro |
In catabolic states of injury and illness, glutamine becomes conditionally-essential (requiring intake from food or supplements). Glutamine is the most abundant naturally occurring, non-essential amino acid in the human body and one of the few amino acids that can directly cross the blood–brain barrier. Glutamine is a key pharmaconutrient in the body's response to stress and injury. Glutamine exerts its protective effects via multiple mechanisms, including direct protection of cells and tissue from injury, attenuation inflammation, and preservation of metabolic function.
|
|---|---|
| In vivo |
Glutamine shows the greatest benefit when administered at doses greater than 0.35 g/kg/day, with optimal benefit potentially occurring at 0.5 g/kg/day.
|
References |
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































