AMPK (AMP-activated protein kinase) plays a pivotal role in the regulation of cellular energy homeostasis as the principal energy sensor in most eukaryotic cells. In response to stress, AMPK activation switches on catabolic pathways that generate ATP while simultaneously inactivating biosynthetic pathways that consume ATP. [show the full text]
AMPK activators/inhibitors
Isoform-selective Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Information | Product Use Citations | Product Validations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
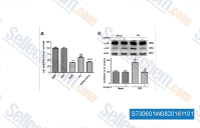
| S7306 | Dorsomorphin Dihydrochloride | Dorsomorphin 2HCl is a potent, reversible, selective AMPK inhibitor with Ki of 109 nM in cell-free assays, exhibiting no significant inhibition of several structurally related kinases including ZAPK, SYK, PKCθ, PKA, and JAK3. Also inhibits type Ⅰ BMP receptor activity. Dorsomorphin induces autophagy in cancer cell line. |
|
|
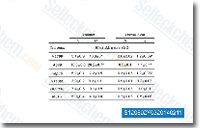
| S1208 | Doxorubicin (Adriamycin) Hydrochloride | Doxorubicin (DOX) HCl is an antibiotic agent that inhibits human DNA topoisomerase II with IC50 of 2.67 μM. Doxorubicin reduces basal phosphorylation of AMPK. Doxorubicin is used in the concomitant treatment of HIV-infected patients but is found to be at high risk of HBV reactivation.This product may precipitate when dissolved in PBS solution. It is recommended to prepare the stock solution in pure water and dilute with either pure water or saline to obtain the working solution.Doxorubicin (Adriamycin) HCl can be used to induce animal models of kidney disease. |
|
|
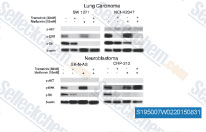
| S1950 | Metformin Hydrochloride | Metformin Hydrochloride (1,1-Dimethylbiguanide Hydrochloride) is a highly effective Antihyperglycemic Agent, which primarily decreases hyperglycemia in hepatocytes by suppressing hepatic gluconeogenesis (glucose production by the liver). It also promotes mitophagy in mononuclear cells and induces apoptosis of lung cancer cells through activating the JNK/p38 MAPK pathway and GADD153. |
|
|
| S8161 | ON123300 | ON123300 is a potent and multi-targeted kinase inhibitor with IC50 of 3.9 nM, 5 nM, 26 nM, 26 nM, 9.2 nM and 11nM for CDK4, Ark5/NUAK1, PDGFRβ, FGFR1, RET (c-RET), and Fyn, respectively. |
|
|
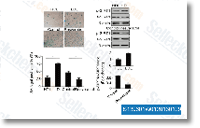
| S1396 | Resveratrol (trans-Resveratrol) | Resveratrol has a wide spectrum of targets including cyclooxygenases(i.e. COX, IC50=1.1 μM), lipooxygenases(LOX, IC50=2.7 μM), kinases, sirtuins and other proteins. It has anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, blood-sugar-lowering and other beneficial cardiovascular effects. Resveratrol induces mitophagy/autophagy and autophagy-dependent apoptosis. |
|
|
| S7840 | Dorsomorphin (Compound C) | Dorsomorphin is a potent, reversible, selective AMPK inhibitor with Ki of 109 nM in cell-free assays, exhibiting no significant inhibition of several structurally related kinases including ZAPK, SYK, PKCθ, PKA, and JAK3. Dorsomorphin selectively inhibits the BMP type I receptors ALK2, ALK3 and ALK6. Dorsomorphin is used in promoting specific cell differentiation and inducing cancer cell line autophagy. For cell testing, the water-soluble S7306 Dorsomorphin (Compound C) 2HCl is recommended. |
|
|
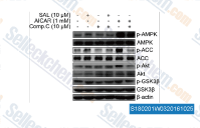
| S1802 | AICAR (Acadesine) | AICAR (Acadesine, NSC105823, AICA Riboside), an AMPK activator, results in accumulation of ZMP, which mimics the stimulating effect of AMP on AMPK and AMPK kinase. This compound induces mitophagy. Phase 3. |
|
|
| S2697 | A-769662 | A-769662 is a potent, reversible AMPK activator with EC50 of 0.8 μM in cell-free assays, little effect on GPPase/FBPase activity. |
|
|
| S5958 | Metformin (1,1-Dimethylbiguanide) | Metformin (1,1-Dimethylbiguanide), a widely used drug for treatment of type 2 diabetes, activates AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) in hepatocytes. Metformin promotes mitophagy in mononuclear cells. Metformin induces apoptosis of lung cancer cells through activating JNK/p38 MAPK pathway and GADD153. |
|
|
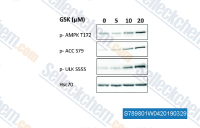
| S7898 | GSK621 | GSK621 is a specific and potent AMPK activator. |
|
|
Signaling Pathway Map
AMPK exists as a heterotrimeric protein complex composed of a catalytic α-subunit (α1 or α2) and regulatory β-subunit (β1 or β2) and γ- subunit (γ1, γ2 or γ3). The structure of the α-subunit consists of a conventional Ser/Thr kinase domain at the N-terminal, an auto-inhibitory domain (AID), an extended linker peptide and the α-subunit C-terminal domain (α-CTD). The β-subunit contains a carbohydrate-binding module (CBM), with the β-subunit C-terminal domain (β-CTD) interacting with both the α-CTD and the amino terminus of the γ-subunit, thus forming the core of the complex. The γ-subunit includes four tandem repeats of a sequence motif, termed a CBS repeat (cystathionine β-synthase, CBS1-4), that forms a flattened disk with one repeat in each quadrant to create four potential ligand binding sites in the centre (site 1-4). AMPK activity increases more than 100-fold when the conserved Thr172 residue in the activation loop of the catalytic α-subunit is phosphorylated by upstream AMPK kinases (AMPKK) such as LKB1 requiring the change in AMP or ADP levels, and CaMKKβ (CaMKK2) in response to increases in cell Ca2+. AMP binding to ligand binding site 1 of the γ subunit allosterically activates the AMPK complex by facilitating the phosphorylation of Thr172 in the catalytic α-subunit, whereas binding of AMP or ADP to site 3 modulates the phosphorylation state of Thr172. In addition to allosteric activation by AMP, the effects on phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of Thr172 can also be produced by ADP, which requires N-terminal myristylation of the β-subunit. [1][2]
AMPK is activated by various types of metabolic stress (glucose deprivation, hypoxia, ischemia, metabolic poisons, or muscle contraction), as well as drugs and xenobiotics (metformin, resveratrol, or berberine) through the classical or canonical mechanisms, which involve increases in cellular AMP, ADP or Ca2+. The metformin for the treatment of people with type 2 diabetes indirectly activates AMPK by increasing cellular AMP and ADP, usually by inhibiting mitochondrial ATP synthesis. Additionally, AMPK activated by resveratrol or metformin upregulates genes involved in oxidative metabolism and oxidative stress resistance by regulating transcription factors of the abnormal dauer formation 16 (DAF-16)/forkhead box O (FOXO) family, contributing to its effects on extending healthy lifespan. Some types of cellular stress such as reactive oxygen species (ROS) and DNA damaging agents (etoposide, doxorubicin and ionizing radiation) activate AMPK by non-canonical mechanisms that involve ATM rather than the increases in AMP, ADP or Ca2+ levels. Activation of AMPK enhances both the transcription and translocation of GLUT4, resulting in an increase in insulin-stimulated glucose uptake. In LKB1-knockout but not AMPKα1-knockout mice, the effects of both AICAR and contraction on glucose uptake are lost. In addition, AMPK also stimulates other catabolic processes such as fatty acid oxidation and glycolysis via inhibition of ACC2 and activation of PFKFB. AMPK is also involved in the regulation of mitochondrial biogenesis through the activation of PGC1α, and the turnover of mitochondria via the special form of autophagy termed mitophagy by activating ULK1, and subsequently triggering autophagy. In addition, mTOR complex-1 (TORC1) can be inhibited by AMPK mediated phosphorylation of both its upstream regulator, TSC2, and the TORC1 subunit Raptor. Consistent with its role in cellular energy homeostasis, AMPK also conserves ATP by switching off almost all anabolic pathways, including the biosynthesis of lipids, carbohydrates, proteins and ribosomal RNA. Moreover, AMPK also functions beyond metabolism through regulation of the cell cycle and modulation of membrane excitability. As LKB1 is a tumor suppressor and is frequently mutated in spontaneous cancers, AMPK-activating drugs such as metformin or A-769662 significantly protect against the development of cancer. [1][2]





































