research use only
Sulfathiazole Anti-infection chemical
Cat.No.S3116
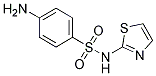
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 255.32
Quality Control
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 51 mg/mL
(199.74 mM)
Water : Insoluble Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 255.32 | Formula | C9H9N3O2S2 |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 72-14-0 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | N/A | Smiles | C1=CC(=CC=C1N)S(=O)(=O)NC2=NC=CS2 | ||
Mechanism of Action
| In vitro |
Sulfathiazole (20 μg/L) starts to be degraded between day 31 and day 38 in one of the two batch reactors containing different wastewater matrices. This compound is degraded at a substantially faster rate than sulfamethoxazole or sulfamethazine in the nitrification process (S3). Recovery from spiked manure slurry samples is 64% for this chemical at pH 9. It has acidity constant of pKa of 7.1and retention times (tR) of 7.8. S/N values for this compound are above 100 at the 1 mg/kg level. Its sorption to inorganic sorbents exhibits pronounced pH dependence consistent with sorbate speciation and sorbent charge properties. The cations of this chemical are most important for sorption to clay minerals, followed by neutral species. It posseses at least five crystalline or polymorphic forms: I, II, III, IV and V. Although both amido and imido forms are possible for the molecule, this compound exists in the solid state in the imido form. This chemical (94.9 mg/L) causes a significant increase in reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation and lipid peroxidation in the presence of ultraviolet B (UV-B) light. Exposure to it and UV-B light causes apparent up-regulation of alpha-esterase, hemoglobin, and vitellogenin mRNA and significantly affect the survival of daphnids.
|
References |
|
|---|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































