research use only
Acamprosate Calcium GABA Receptor agonist
Cat.No.S3748
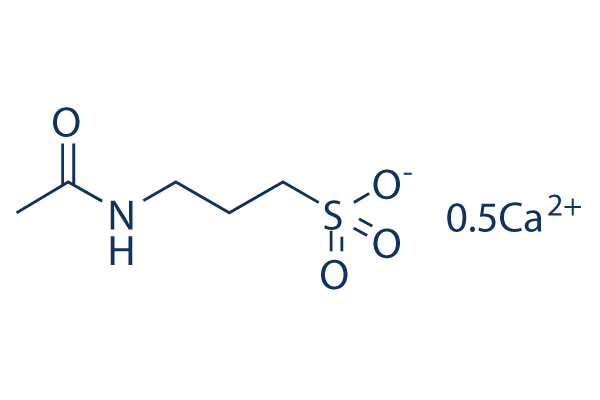
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 200.24
Quality Control
| Related Targets | CFTR CRM1 CD markers AChR Calcium Channel Sodium Channel Potassium Channel TRP Channel ATPase GluR |
|---|---|
| Other GABA Receptor Inhibitors | Dihydromyricetin CGP52432 Ginkgolide A 4-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) SR95531 Chinese Arborvilea Seed Extract Afoxolaner Homotaurine (+)-Borneol L-DAB HBR |
Solubility
|
In vitro |
Water : 40 mg/mL
DMSO
: Insoluble
Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 200.24 | Formula | C5H11NO4S.1/2Ca |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 77337-73-6 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | N-Acetylhomotaurine Calcium, calcium acetylhomotaurinate,N-acetylhomotaurinate | Smiles | CC(=O)NCCCS(=O)(=O)[O-].CC(=O)NCCCS(=O)(=O)[O-].[Ca+2] | ||
Mechanism of Action
| In vitro |
Acamprosate binds to a specific spermidine-sensitive site that modulates the NMDA receptor in a complex way. |
|---|---|
| In vivo |
Acamprosate is absorbed via the gastrointestinal tract, with pharmacokinetic linearity in terms of dose and time. Absolute bioavailability of acamprosate under fasting conditions is approximately 11%. After food intake, bioavailability decreases by approximately 20%, but this decrease lacks clinical significance. Steady-state plasma concentrations of acamprosate are reached within 5 days of dosing and the terminal half-life ranges from 20–33 hours following the standard 2 × 333 dosing regime. Plasma protein binding is negligible. Acamprosate is not metabolized in the liver and is excreted unchanged in the urine. Acamprosate may have neuroprotective effects. Acamprosate appears to work by normalizing the dysregulation of NMDA-mediated glutamatergic neurotransmission that occurs during chronic alcohol consumption and withdrawal, and thus attenuates one of the physiological mechanisms that may prompt relapse. |
References |
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































