research use only
Adrenalone HCl Adrenergic Receptor agonist
Cat.No.S3185
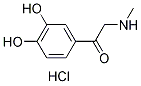
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 217.65
Quality Control
| Related Targets | AChR 5-HT Receptor COX Calcium Channel Histamine Receptor Dopamine Receptor GABA Receptor TRP Channel Cholinesterase (ChE) GluR |
|---|---|
| Other Adrenergic Receptor Inhibitors | Zenidolol (ICI-118551) Hydrochloride L755507 Yohimbine HCl Atipamezole Higenamine hydrochloride Detomidine HCl Naftopidil Demethyl-Coclaurine Buflomedil HCl Fenoterol hydrobromide |
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 44 mg/mL
(202.15 mM)
Water : 44 mg/mL Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 217.65 | Formula | C9H11NO3.HCl |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 62-13-5 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | N/A | Smiles | CNCC(=O)C1=CC(=C(C=C1)O)O.Cl | ||
Mechanism of Action
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
α1-adrenergic receptor
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Adrenalone (12 μM) inhibits conversion of dopamine to norepinephrine by inhibiting dopamine β oxidase. The structure of Adrenalone differs from epinine only in that the former possesses a ketone group in the β position. The reduction of adrenalone (0.1 mM) by hydrated electrons in nitrogenated aqueous solutions containing either 10 or 100 mM tert-butyl alcohol results in identical transient spectra, therefore all OH radicals have been scavenged. While adrenalone behaves like a carbonyl compound during reduction, oxidation reactions are primarily governed by the catechol functional group. Adrenalone, which is a topical nasal decongestant, hemostatic, and vasoconstrictor, is a keton form of the natural substrate epinephrine. Adrenalone contains an aromatic ring that forms hydrophobic interactions with Phe72, Tyr152, and Phe317, an amine group that forms an ionic bond with Asp75, and a hydroxyl group that forms a hydrogen bond with Ala145. Adrenalone at 10 μM (100 μM) reduces substrate uptake to 99% (27%).
|
| In vivo |
Adrenalone (0.05%) administrated topically to the eyes of rabbits at 30 min intervals results in concentration of 7.75 mg/kg, 0.87 mg/kg and 2.51 mg/kg in cornea, aqueous humor and iris-ciliary body, respectively.
|
References |
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































