research use only
Fatostatin HBr SREBP inhibitor
Cat.No.S8284
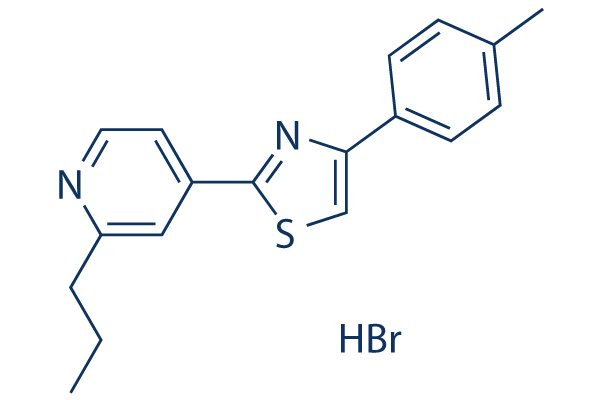
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 375.33
Quality Control
| Related Targets | Dehydrogenase HSP Transferase P450 (e.g. CYP17) PDE phosphatase PPAR Vitamin Carbohydrate Metabolism Mitochondrial Metabolism |
|---|---|
| Other SREBP Inhibitors | Cinobufotalin |
Cell Culture, Treatment & Working Concentration
| Cell Lines | Assay Type | Concentration | Incubation Time | Formulation | Activity Description | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CHO-K1 cells | Function assay | 20 h | Inhibition of SREBP2 activation expressed in CHO-K1 cells co-transfected with pSRE-Luc plasmid assessed as inhibition of luciferase expression after 20 hrs by luciferase reporter gene assay, IC50=5.6 μM | 21561152 | ||
| mouse hepatocytes | Function assay | 1 uM | 90 mins | Metabolic stability in mouse hepatocytes at 1 uM after 90 mins by LC-MS/MS analysis | 21561152 | |
| InhA cells | Antimicrobial assay | Antimicrobial activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv over-expressing InhA cells assessed as upshift of MIC relative to wild type | 24967731 | |||
| Click to View More Cell Line Experimental Data | ||||||
Solubility
|
In vitro |
Ethanol : 58 mg/mL
DMSO
: 7 mg/mL
(18.65 mM)
Water : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 375.33 | Formula | C18H18N2S·HBr |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 298197-04-3 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | 125B11 HBr | Smiles | CCCC1=NC=CC(=C1)C2=NC(=CS2)C3=CC=C(C=C3)C.Br | ||
Mechanism of Action
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
SREBPs
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Fatostatin inhibits the insulin-induced adipogenesis of 3T3-L1 cells and the serum-independent growth of human androgen-independent prostate cancer (DU145) cells. Fatostatin blocks the activation of SREBPs in cells in tissue culture. Fatostatin suppresses cell proliferation and anchorage-independent colony formation in both androgen-responsive LNCaP and androgen-insensitive C4-2B prostate cancer cells. Fatostatin also reduced in vitro invasion and migration in both cell lines. Further, fatostatin causes G2/M cell cycle arrest and induces apoptosis by increasing caspase-3/7 activity and the cleavages of caspase-3 and PARP. |
| In vivo |
Fatostatin blocks increases in body weight, blood glucose, and hepatic fat accumulation in obese ob/ob mice, even under uncontrolled food intake. Fatostatin significantly inhibits subcutaneous C4-2B tumor growth and markedly decreases serum PSA level compared to the control group. |
References |
|
Applications
| Methods | Biomarkers | Images | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western blot | p-SREBP-1 / N-SREBP-1 / p-SREBP-2 / N-SREBP-2 / FASN / HMGCR AR / PSA Cyclin B / PH3 |
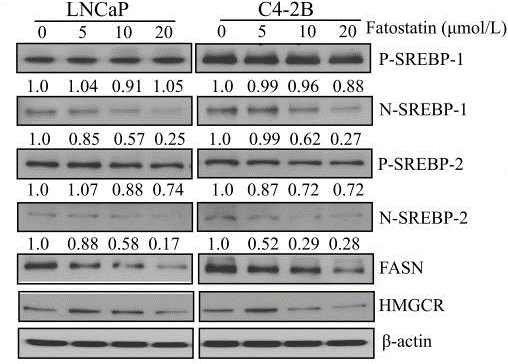
|
24493696 |
| Immunofluorescence | α-tubulin / centromere |
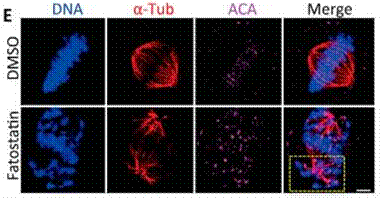
|
27378817 |
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell viability |
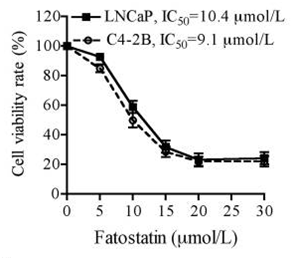
|
24493696 |
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































