- Inhibitors
- Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
TDO2 Antibody [L23B14]
Cat.No.: F4553
Application:
Reactivity:
Usage Information
| Dilution |
|---|
|
| Application |
|---|
| WB |
| Reactivity |
|---|
| Human |
| Source |
|---|
| Mouse Monoclonal Antibody |
| Storage Buffer |
|---|
| PBS, pH 7.2+50% Glycerol+0.05% BSA+0.01% NaN3 |
| Storage (from the date of receipt) |
|---|
| -20°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles), 2 years |
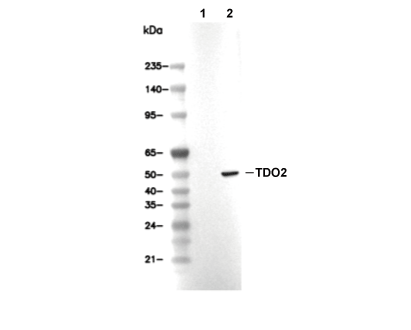
| Observed MW |
|---|
| 47.7 kDa |
| *Why do the predicted and actual molecular weights differ? The following reasons may explain differences between the predicted and actual protein molecular weight. |
Biological Description
| Specificity |
|---|
| TDO2 Antibody [L23B14] detects endogenous levels of total TDO2 protein. |
| Clone |
|---|
| L23B14 |
| Synonym(s) |
|---|
| chky; TDO; TDO2; TDOTO; TO; TPH2EC 1.13.11.11; TRPO; TRPOtryptophanase; Tryptamin 2,3-dioxygenase; tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase; Tryptophan Oxygenase; Tryptophan Pyrrolase; Tryptophanase |
| Background |
|---|
| TDO2 (tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase), encoded by the TDO2 gene, functions as a heme-dependent homotetrameric enzyme catalyzing the initial, rate-limiting step of the kynurenine pathway by oxidizing L-tryptophan to N-formylkynurenine (hydrolyzed to kynurenine), thereby controlling systemic tryptophan catabolism predominantly in the liver with inducible expression in brain and tumors. It comprises four ~47 kDa subunits (406 aa each) in a dimer-of-dimers assembly featuring an all-α-helical fold; each monomer harbors a protoporphyrin IX heme bidentally coordinated by proximal His328 in a four-helix bundle active site, with substrate docking enabled by Arg144 (polarizes indole), Phe72/His76 (hydrophobic clamp), and N-terminal loops mediating positive cooperativity. TDO2 homotropically activates via Trp-induced conformational shifts propagating across interfaces, depleting local Trp to curb serotonin/melatonin while channeling flux to NAD+ biosynthesis and immunoregulatory kynurenines, Kyn binds/dimerizes AhR, translocating it to induce IDO1, TGF-β, IL-10 for T-cell anergy, Treg expansion, and M2 macrophage polarization; disease-wise, TDO2 overexpression in gliomas, breast, and colorectal cancers exploits this axis for tumor immune evasion (correlating with poor survival), while in neurodegeneration (Alzheimer's, schizophrenia), excess quinolinic acid drives NMDA-mediated excitotoxicity. |
| References |
|---|
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.