research use only
Tubeimoside I Apoptosis related chemical
Cat.No.S3814
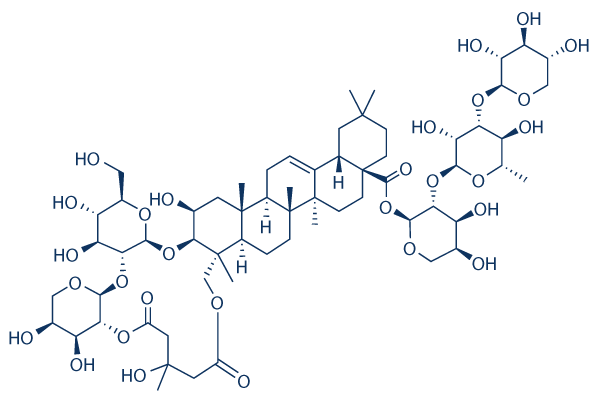

Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 1319.43
Quality Control
| Related Targets | Bcl-2 Caspase PD-1/PD-L1 Ferroptosis p53 Synthetic Lethality STAT TNF-alpha Ras KRas |
|---|---|
| Other Apoptosis related Inhibitors | Importazole Genipin Pitstop 2 Plumbagin 6-Gingerol Crocin Colcemid Euphorbia factor L3 Sophoridine Pomolic acid |
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 100 mg/mL
(75.79 mM)
|
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 1319.43 | Formula | C63H98O29 |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 102040-03-9 | -- | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | Lobatoside H | Smiles | CC1C(C(C(C(O1)OC2C(C(COC2OC(=O)C34CCC(CC3C5=CCC6C(C5(CC4)C)(CCC7C6(CC(C8C7(COC(=O)CC(CC(=O)OC9C(C(COC9OC1C(C(C(OC1O8)CO)O)O)O)O)(C)O)C)O)C)C)(C)C)O)O)O)OC1C(C(C(CO1)O)O)O)O | ||
Mechanism of Action
| In vitro |
TBMS I inhibits the proliferation of both HepG2 and L-02 cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner, but HepG2 cells appear more sensitive to the agent. When exposed to TBMS I for 24, 48 and 72 h, IC50 for HepG2 cells versus L-02 cells are 15.5 vs. 23.1, 11.7 vs. 16.2, 9.2 vs. 13.1 (μM, p<0.01), respectively. TBMS I induces cell shrinkage, nuclear condensation and fragmentation, cell cycle arrest at the G2/M phase, mitochondrial membrane disruption, release of cytochrome c from the mitochondria, activation of caspase 3 and 9, and shifting Bax/Bcl-2 ratio from being anti-apoptotic to pro-apoptotic, all indicative of initiation and progression of apoptosis involving mitochondrial dysfunction.
|
|---|---|
| In vivo |
TBMS1 significantly inhibits the production of the pro-inflammatory cytokines, TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β in vitro and in vivo. Pretreatment with TBMS1 markedly attenuates the development of pulmonary edema, histological severities and inflammatory cells infiltration in mice with acute lung injury (ALI). TBMS1 exerts an anti-inflammatory effect in vivo model of ALI through suppression of IkB activation and p38/extracellular signal-regulated kinase mitogen-activated protein kinases signaling in a dose-dependent manner. TBMS1 could be a potent anti-tumor agent by inducing apoptosis in a variety of cancer types via the mitochondrial-related signaling pathway.
|
References |
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































