B-raf plays crucial roles in MAPK signaling pathway, ErbB signaling pathway, Insulin signaling pathway and mTOR signaling pathway which have effect on cell survival, growth and differentiation. RAF can be regulated by RAS and PKC. [show the full text]
Raf Inhibitors
Isoform-selective Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Information | Product Use Citations | Product Validations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
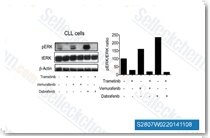
| S2807 | Dabrafenib (GSK2118436) | Dabrafenib is a mutant BRAFV600E specific inhibitor with IC50 of 0.7 nM in cell-free assays, with 7- and 9-fold less potency against B-Raf(wt) and c-Raf, respectively. |
|
|
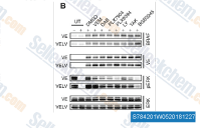
| S7842 | LY3009120 | LY3009120 (DP-4978) is a potent pan-Raf inhibitor with IC50 of 44 nM, 31-47 nM, and 42 nM for A-raf, B-Raf, and C-Raf in A375 cells, respectively. This compound induces autophagy. Phase 1. |
|
|
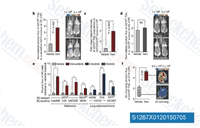
| S1267 | PLX4032 (Vemurafenib) | Vemurafenib (PLX4032, RG7204, RO5185426) is a novel and potent inhibitor of B-RafV600E with IC50 of 31 nM in cell-free assay. 10-fold selective for B-RafV600E over wild-type B-Raf in enzymatic assays and the cellular selectivity can exceed 100-fold. Vemurafenib (PLX4032, RG7204) induces autophagy. |
|
|
| E1649 | Exarafenib (KIN-2787) | Exarafenib(KIN-002787, KIN-2787, RAF/KIN_2787) is an orally-available, selective inhibitor of pan-RAF. Exarafenib is effective in RAF-dependent cancers, including all classes of BRAF alterations. Exarafenib suppresses MAPK signaling in RAF-dependent melanoma cell lines. KIN-2787 exhibits low nanomolar to picomolar potency against RAF1, BRAF, and ARAF with an IC50 of 0.06-3.46 nM with minimal activity towards non-RAF kinases. | ||
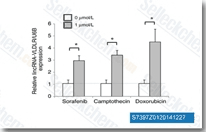
| S7397 | Sorafenib (BAY 43-9006) | Sorafenib is a multikinase inhibitor of Raf-1 and B-Raf with IC50 of 6 nM and 22 nM in cell-free assays, respectively. Sorafenib inhibits VEGFR-2, VEGFR-3, PDGFR-β, Flt-3 and c-KIT with IC50 of 90 nM, 20 nM, 57 nM, 59 nM and 68 nM, respectively. Sorafenib induces autophagy and apoptosis and activates ferroptosis with anti-tumor activity. |
|
|
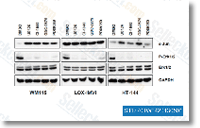
| S1104 | GDC-0879 | GDC-0879 (AR-00341677) is a novel, potent, and selective B-Raf inhibitor with IC50 of 0.13 nM in A375 and Colo205 cells with activity against c-Raf as well; no inhibition known to other protein kinases. |
|
|
| S7170 | Avutometinib (Ro5126766, CH5126766) | Avutometinib(RO5126766,CH5126766,VS 6766, CKI-27, R-7304, RG-7304) is a dual RAF/MEK inhibitor with IC50 of 8.2 nM,19 nM, 56 nM, and 160 nM for BRAF V600E, BRAF, CRAF, and MEK1, respectively. Phase 1. |
|
|
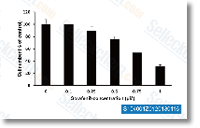
| S1040 | Sorafenib Tosylate (BAY 43-9006) | Sorafenib tosylate is a multikinase inhibitor of Raf-1 and B-Raf with IC50 of 6 nM and 22 nM in cell-free assays, respectively. Sorafenib Tosylate inhibits VEGFR-2, VEGFR-3, PDGFR-β, Flt-3 and c-KIT with IC50 of 90 nM, 20 nM, 57 nM, 59 nM and 68 nM, respectively. Sorafenib Tosylate induces autophagy and apoptosis and activates ferroptosis with anti-tumor activity. |
|
|
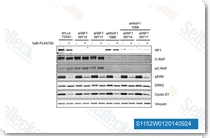
| S1152 | PLX-4720 | PLX4720 is a potent and selective inhibitor of B-RafV600E with IC50 of 13 nM in a cell-free assay, equally potent to c-Raf-1(Y340D and Y341D mutations), 10-fold selectivity for B-RafV600E than wild-type B-Raf. |
|
|
| S5069 | Dabrafenib Mesylate | Dabrafenib Mesylate (GSK2118436) is the mesylate salt form of dabrafenib, an orally bioavailable inhibitor of B-raf (BRAF) protein with IC50s of 0.8 nM, 3.2 nM and 5 nM for B-Raf (V600E), B-Raf (WT) and C-Raf, respectively. |
|
|
Signaling Pathway Map
RAF kinase signaling is highlighted in the RAS-RAF-MEK-ERK signal transduction cascade. Activated RAS kinase signaling results in the activation of RAF proteins. Following these events, MEK1 and MEK2 dual specificity protein kinases become phosphorylated and activated. It should be noted that RAF kinases display restricted substrate specificity for these MEK enzymes. The RAF family of protein-serine/threonine kinases comprise of A-RAF, B-RAF, and C-RAF oncogenes originally discovered in the early 1980s. RAF family proteins function as six dimeric members, either in homo- and heterodimer formation. Since there are four RAS members, the total number of RAS-RAF interactions is equivalent to twenty-four. And downstream, with two MEK members available the total number of interactions between RAF-MEK constituents is twelve.[1]
All RAF kinases share three conserved regions (CR): CR1, CR2, and CR3. CR1 consists of cysteine-rich domain (binds to two zinc ions) and a RAS-binding domain. These properties facilitate CR1 interaction with RAS and phospholipids in the membrane. CR2, is a serine/threonine rich domain that facilitates the binding of regulatory protein 14-3-3 upon phosphorylation – this result in inactivation. At the C-terminus is the protein kinase domain, CR3, which contains a downstream stimulatory 14-3-3 binding site. Regulating RAF kinase activity are a number of protein-protein interactions, phosphorylation, dephosphorylation and conformational changes. In their inactivated state, most RAF proteins are found in the cytosol.[1]
It was not until 2002, that B-RAF mutations were noted in cancer cells lines. Most notably, B-RAF has been associated with melanomas and papillary thyroid, ovarian, and colorectal tumors. And to a lesser degree cancers of the lung, pancreas, and bladder have also been found to have aberrant B-RAF activity. Consequently, since B-RAF mutations are involved in several different cancer types it is believed that B-RAF functions as an oncogene driver. In clinical trials, the first RAF inhibitor was Bayer’s Sorafenib (Nexavar). The compound was found to be effective in restricting tumor activity in renal cell carcinoma and hepatocellular cancers and is currently in use for these indications. Recently, PLX4032 was discovered to be a highly selective RAF inhibitor (Roche) and is currently in advanced clinical trials for testing against melanomas.[2]





































