research use only
BHQ ADC Cytotoxin inhibitor
Cat.No.S3628
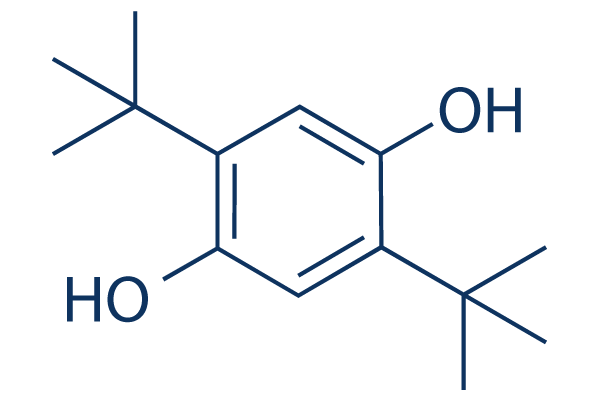
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 222.32
Quality Control
| Related Targets | CFTR CRM1 CD markers AChR Calcium Channel Sodium Channel Potassium Channel GABA Receptor TRP Channel ATPase |
|---|---|
| Other ADC Cytotoxin Inhibitors | SN-38 Triptolide (+)-Bicuculline Rutin Artemisinin Pinocembrin Harmine hydrochloride Psoralen Lappaconite HBr Luteoloside |
Solubility
|
In vitro |
Ethanol : 40 mg/mL
DMSO
: 10 mg/mL
(44.98 mM)
Water : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 222.32 | Formula | C14H22O2 |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 88-58-4 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | 2,5-di-t-butyl-1,4-benzohydroquinone | Smiles | CC(C)(C)C1=CC(=C(C=C1O)C(C)(C)C)O | ||
Mechanism of Action
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
SERCA
66.7 μM
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
2,5-Di-t-butyl-1,4-benzohydroquinone (BHQ) has been described as a rather selective sarco-endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase (SERCA) inhibitor. However, this compound is not very specific, as it hits other sites of action besides SERCA. It is shown, in fact, to reduce passive Ca2+ leakage from internal stores of permeabilized A7r5 vascular smooth muscle cells and to inhibit plasma membrane Ca2+ influx in parotid acinar cells, rat thymic lymphocytes, and GH3 pituitary cells. This chemical affects both endothelial and smooth muscle functions in rat aorta rings in vitro. It induces endothelium-dependent relaxation by stimulating the NO synthase pathway, via activation of Ca2+ influx through Ni2+-sensitive Ca2+ channels in the endothelial cells. This compound exhibits pleiotypic effects on rings deprived of endothelium by inducing both a myotonic response, dependent on the activation of Ca2+ influx via a Ni2+-sensitive pathway, and a myolytic effect, possibly dependent on either the depletion of intracellular Ca2+ stores or antagonism of Ca2+ entry via L-type Ca2+ channels. It is a lipophilic, membrane permeable molecule, capable of generating superoxide anion at both sides of the plasmalemma.
|
References |
Clinical Trial Information
(data from https://clinicaltrials.gov, updated on 2024-05-22)
| NCT Number | Recruitment | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT03791086 | Recruiting | Bronchiectasis Adult |
University of Dundee |
November 1 2019 | -- |
| NCT01302886 | Completed | Smoldering Multiple Myeloma |
Novartis Pharmaceuticals|Novartis |
May 2011 | Phase 2 |
| NCT00741377 | Completed | Multiple Myeloma Bone Disease |
Novartis Pharmaceuticals|Novartis |
January 2009 | Phase 1 |
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































