research use only
WNK463 Serine/threonin kinase inhibitor
Cat.No.S8358
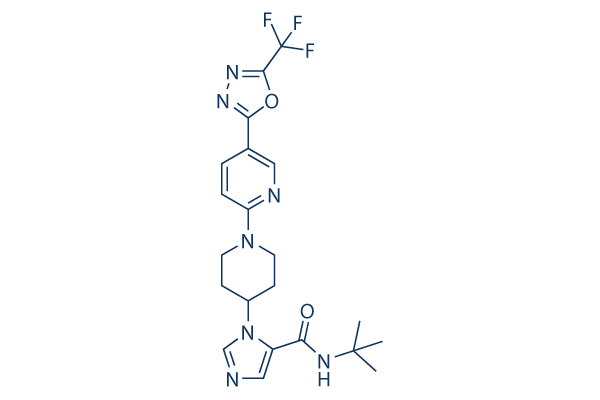
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 463.46
Quality Control
| Related Targets | Bcl-2 Caspase PD-1/PD-L1 Ferroptosis p53 Apoptosis related Synthetic Lethality STAT TNF-alpha Ras |
|---|---|
| Other Serine/threonin kinase Inhibitors | GCN2iB SRPIN340 Benzamidine HCl SPHINX31 BAY-1816032 ML281 DCLK1-IN-1 SGC-GAK-1 WNK-IN-11 MKI-1 |
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 92 mg/mL
(198.5 mM)
Ethanol : 92 mg/mL Water : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 463.46 | Formula | C21H24F3N7O2 |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 2012607-27-9 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | N/A | Smiles | CC(C)(C)NC(=O)C1=CN=CN1C2CCN(CC2)C3=NC=C(C=C3)C4=NN=C(O4)C(F)(F)F | ||
Mechanism of Action
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
WNK2
1nM
WNK1
5nM
WNK3
6nM
WNK4
9nM
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
WNK463 potently inhibited the in vitro kinase activity of all four WNK family members (WNK1, WNK2, WNK3, and WNK4). This compound also inhibited WNK1-catalyzed phosphorylation of the native WNK substrate, oxidative stress response 1 (OSR1) in a biochemical assay and in human embryonic kidney 293 (HEK293) cells that express exogenous OSR1 and that are activated by sorbitol-mediated osmotic stress. |
| In vivo |
In rodent models of hypertension, WNK463 affects blood pressure and body fluid and electrolyte homeostasis. This compound is orally bioavailable in C57BL/6 mice (100%) and Sprague Dawley rats (74%), with a half-life of 3.6 and 2.1 h, respectively. In spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHRs), this compound administered orally (p.o.) at 1, 3, or 10 mg per kg body weight (mg/kg) p.o. achieved maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) values of 88, 441, and 1,170 nM, respectively. These exposures produced dose-dependent decreases in blood pressure and simultaneous increases in heart rate in conscious SHRs. Moreover, this chemical produced significant and dose-dependent increases in urine output as well as urinary sodium and potassium excretion rates. Orally administered this compound also significantly decreased blood pressure in these hypertensive mice. It elicited in vivo cardiovascular and renal effects through WNK kinase inhibition. |
References |
|
Applications
| Methods | Biomarkers | Images | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western blot | pSPAK/pOSR1 |
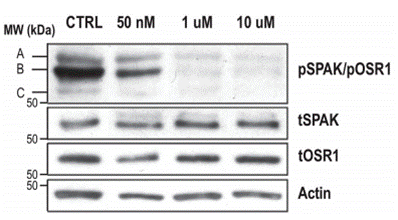
|
31207112 |
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































