- Inhibitors
- Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
Vincamine
Cat.No.S3891
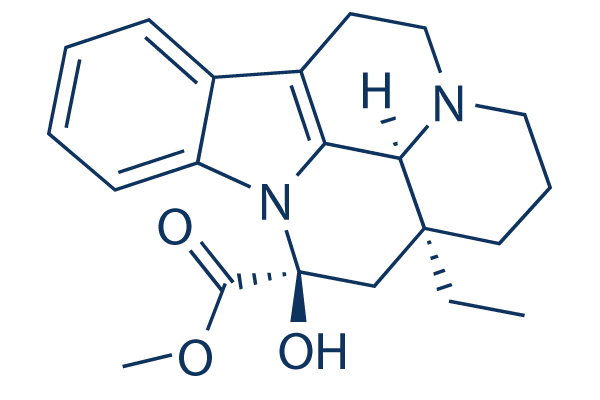
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 354.44
Jump to
Quality Control
Batch:
Purity:
99.87%
99.87
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 3 mg/mL
(8.46 mM)
|
Molarity Calculator
Dilution Calculator
Molecular Weight Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
mg/kg
g
μL
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
%
DMSO
%
%
Tween 80
%
ddH2O
%
DMSO
+
%
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 354.44 | Formula | C21H26N2O3 |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 1617-90-9 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | Angiopac, Devincan, Equipur, Minorin, Novicet, Oxybral, Perval, Sostenil, Tripervan | Smiles | CCC12CCCN3C1C4=C(CC3)C5=CC=CC=C5N4C(C2)(C(=O)OC)O | ||
Mechanism of Action
| In vitro |
Vincamine decreases amyloid-β 25-35 induced oxidative stress and reduces reactive oxygen species levels. It significantly reduces the rate of apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner. This compound could provide neuroprotection from Aβ25-35 induced PC12 apoptosis through the phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase/Akt signaling pathway.
|
|---|---|
| In vivo |
Vincamine could cross the blood-brain barrier, and its antioxidant scavenging capacity to inactivate hydroxyl free radicals is actually ranked in part with Vitamin E. This compound decreases the mean arterial blood pressure (by 5-35%), the cardial output and the heart rate. After oral application of 20 mg/kg vincamine in rats, this chemical is rapidly absorbed and eliminated. The apparent elimination half life is 1.71 h. The bioavailability of this compound after oral administration is 58% suggesting a significant firstpass metabolism. It is taken up in a high concentration by the different organs, the maximal organ-plasma concentration ratio is 21 for lungs, 14.6 for brain, 14.3 for the kidneys, 8.9 for the liver and 7.6 for the heart. There is no steady-state between plasma and heart, lungs and brain, the elimination from these organs is significantly more rapid than from plasma. This chemical is mainly metabolized in the liver and excreted by the kidneys and it may also go through cerebral metabolism. In the pharmacokinetic profile of vincamine, the compound is about 64% bound to plasma proteins, and 6% bound to erythrocytes.
|
References |
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































