- Inhibitors
- Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
Thiostrepton
Cat.No.S4354
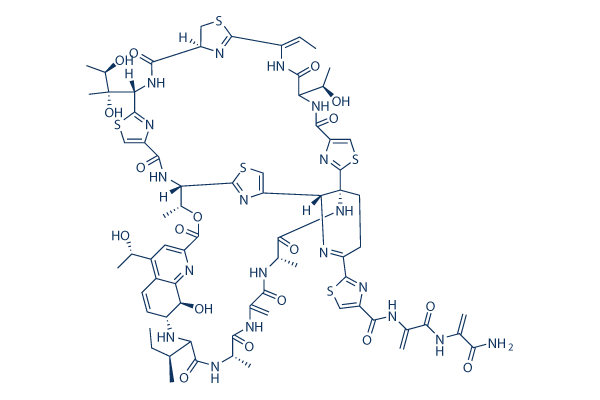
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 1664.89
Jump to
Quality Control
Batch:
Purity:
99.86%
99.86
Solubility
|
In vitro |
|
Molarity Calculator
Dilution Calculator
Molecular Weight Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
mg/kg
g
μL
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
%
DMSO
%
%
Tween 80
%
ddH2O
%
DMSO
+
%
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 1664.89 | Formula | C72H85N19O18S5 |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 1393-48-2 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | Alaninamide, Bryamycin, Thiactin | Smiles | CCC(C)C1C(=O)NC(C(=O)NC(=C)C(=O)NC(C(=O)NC23CCC(=NC2C4=CSC(=N4)C(C(OC(=O)C5=NC6=C(C=CC(C6O)N1)C(=C5)C(C)O)C)NC(=O)C7=CSC(=N7)C(NC(=O)C8CSC(=N8)C(=CC)NC(=O)C(NC(=O)C9=CSC3=N9)C(C)O)C(C)(C(C)O)O)C1=NC(=CS1)C(=O)NC(=C)C(=O)NC(=C)C(=O)N)C)C | ||
Mechanism of Action
| In vitro |
Thiostrepton inhibits growth of the parasite in the micromolar range which is 10-fold below concentrations with observable effects on total protein synthesis. This compound results in disappearance of organellar-encoded RNA transcripts within 6 hours of treatment while transcripts of a nuclear-encoded mRNA remain constant for at least 8 hous of treatment. It directly interacts with two nucleotides in the GTPase domain of Escherichia coli. This chemical directly interacts the region around position 1067 in domain II of 23S rRNA inhibits GTP hydrolysis by elongation factor G (EF-G) on the ribosome at the conditions of multiple turnover. It interferes with EF-G footprints in the alpha-sarcin stem loop (A2660, A2662) located in domain VI of 23S rRNA. The compound interacts with a 58-nucleotide domain of large subunit ribosomal RNA, and binds to the ribosome cooperatively with Ribosomal protein L11. Its and RNA recognition cooperativity can be attributed to N- and C-terminal domains of L11, respectively. It binds primarily to 23 S rRNA, thus probably inhibits peptide elongation by impeding a conformational change within protein L11 that is important for the function of the ribosomal GTPase centre. Treatment with this compound (10 μM) reduces FOXM1 expression in a time- and dose-dependent manner, independent of de novo protein synthesis and predominantly at transcriptional and gene promoter levels. It (10 μM) induces cell cycle arrest at G(1) and S phases and cell death, concomitant with FOXM1 repression in breast cancer cells. This agent (10 μM) also shows efficacy in repressing breast cancer cell migration, metastasis, and transformation, which are all downstream functional attributes of FOXM1.
|
References |
|
|---|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































