- Inhibitors
- Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
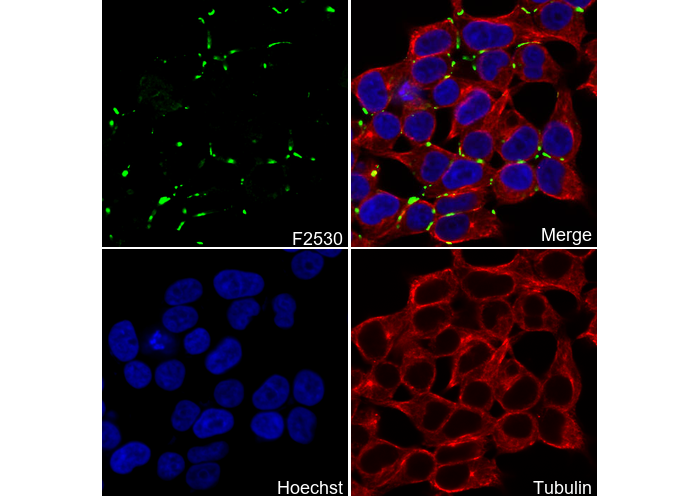
ZO1 tight junction protein Antibody [A24G22]
Cat.No.: F2530
Application:
Reactivity:
Usage Information
| Dilution |
|---|
|
| Application |
|---|
| IHC, IF, FCM |
| Reactivity |
|---|
| Rat, Human, Mouse |
| Source |
|---|
| Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody |
| Storage Buffer |
|---|
| PBS, pH 7.2+50% Glycerol+0.05% BSA+0.01% NaN3 |
| Storage (from the date of receipt) |
|---|
| -20°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles), 2 years |
| Positive Control | Human kidney tissue; Human breast cancer tissue; Rat spleen tissue; Mouse kidney tissue; MCF7 cell; HEK-293 cell |
|---|---|
| Negative Control |
Exprimental Methods
| IF |
|---|
Experimental Protocol:
Sample Preparation
1. Adherent Cells: Place a clean, sterile coverslip in a culture dish. Once the cells grow to near confluence as a monolayer, remove the coverslip for further use.
2. Suspension Cells: Seed the cells onto a clean, sterile slide coated with poly-L-lysine.
3. Frozen Sections: Allow the slide to thaw at room temperature. Wash it with pure water or PBS for 2 times, 3 minutes each time.
4. Paraffin Sections: Deparaffinization and rehydration. Wash the slide with pure water or PBS for 3 times, 3 minutes each time. Then perform antigen retrieval.
Fixation
1. Fix the cell coverslips/spots or tissue sections at room temperature using a fixative such as 4% paraformaldehyde (4% PFA) for 10-15 minutes.
2. Wash the sample with PBS for 3 times, 3 minutes each time.
Permeabilization
1.Add a detergent such as 0.1–0.3% Triton X-100 to the sample and incubate at room temperature for 10–20 minutes.
(Note: This step is only required for intracellular antigens. For antigens expressed on the cell membrane, this step is unnecessary.)
Wash the sample with PBS for 3 times, 3 minutes each time.
Blocking
Add blocking solution and incubate at room temperature for at least 1 hour. (Common blocking solutions include: serum from the same source as the secondary antibody, BSA, or goat serum.)
Note: Ensure the sample remains moist during and after the blocking step to prevent drying, which can lead to high background.
Immunofluorescence Staining (Day 1)
1. Remove the blocking solution and add the diluted primary antibody.
2. Incubate the sample in a humidified chamber at 4°C overnight.
Immunofluorescence Staining (Day 2)
1. Remove the primary antibody and wash with PBST for 3 times, 5 minutes each time.
2. Add the diluted fluorescent secondary antibody and incubate in the dark at 4°C for 1–2 hours.
3. Remove the secondary antibody and wash with PBST for 3 times, 5 minutes each time.
4. Add diluted DAPI and incubate at room temperature in the dark for 5–10 minutes.
5. Wash with PBST for 3 times, 5 minutes each time.
Mounting
1. Mount the sample with an anti-fade mounting medium.
2. Allow the slide to dry at room temperature overnight in the dark.
3. Store the slide in a slide storage box at 4°C, protected from light.
|
| IHC |
|---|
Experimental Protocol:
Deparaffinization/Rehydration
1. Deparaffinize/hydrate sections:
2. Incubate sections in three washes of xylene for 5 min each.
3. Incubate sections in two washes of 100% ethanol for 10 min each.
4. Incubate sections in two washes of 95% ethanol for 10 min each.
5. Wash sections two times in dH2O for 5 min each.
6.Antigen retrieval: For Citrate: Heat slides in a microwave submersed in 1X citrate unmasking solution until boiling is initiated; continue with 10 min at a sub-boiling temperature (95°-98°C). Cool slides on bench top for 30 min.
Staining
1. Wash sections in dH2O three times for 5 min each.
2. Incubate sections in 3% hydrogen peroxide for 10 min.
3. Wash sections in dH2O two times for 5 min each.
4. Wash sections in wash buffer for 5 min.
5. Block each section with 100–400 µl of blocking solution for 1 hr at room temperature.
6. Remove blocking solution and add 100–400 µl primary antibody diluent in to each section. Incubate overnight at 4°C.
7. Remove antibody solution and wash sections with wash buffer three times for 5 min each.
8. Cover section with 1–3 drops HRPas needed. Incubate in a humidified chamber for 30 min at room temperature.
9. Wash sections three times with wash buffer for 5 min each.
10. Add DAB Chromogen Concentrate to DAB Diluent and mix well before use.
11. Apply 100–400 µl DAB to each section and monitor closely. 1–10 min generally provides an acceptable staining intensity.
12. Immerse slides in dH2O.
13. If desired, counterstain sections with hematoxylin.
14. Wash sections in dH2O two times for 5 min each.
15. Dehydrate sections: Incubate sections in 95% ethanol two times for 10 sec each; Repeat in 100% ethanol, incubating sections two times for 10 sec each; Repeat in xylene, incubating sections two times for 10 sec each.
16. Mount sections with coverslips and mounting medium.
|
Biological Description
| Specificity |
|---|
| ZO1 tight junction protein Antibody [A24G22] detects endogenous levels of total ZO1 tight junction protein. |
| Subcellular Location |
|---|
| Cell junction, Cell membrane, Cell projection, Gap junction, Membrane, Tight junction |
| Uniprot ID |
|---|
| Q07157 |
| Clone |
|---|
| A24G22 |
| Synonym(s) |
|---|
| ZO1; TJP1; Tight junction protein ZO-1; Tight junction protein 1; Zona occludens protein 1; Zonula occludens protein 1 |
| Background |
|---|
| ZO-1 (Zonula Occludens-1) is a peripheral membrane phosphoprotein belonging to the membrane-associated guanylate kinase (MAGUK) family and serves as a critical scaffolding molecule in tight junctions. ZO-1 contains three PDZ domains that facilitate protein-protein interactions, an SH3 domain that binds various signaling proteins, and a guanylate kinase (GuK) domain connected by flexible hinge regions; its unique C-terminal region directly binds to the actin cytoskeleton, anchoring the tight junction complex to maintain cellular integrity. ZO-1 organizes transmembrane tight junction proteins such as occludin and claudins, linking them to cytosolic partners like ZO-2 and ZO-3, thus playing an essential role in assembling and maintaining the tight junction barrier that controls paracellular permeability. ZO-1 also acts as a signaling hub regulating cell growth, migration, angiogenesis, and inflammation and helps maintain epithelial cell polarity by preserving the boundary between apical and basolateral membrane domains. ZO-1 is vital for tissue homeostasis in barriers like intestinal epithelium and the blood-brain barrier, with its downregulation associated with diseases such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and cancer progression, where compromised tight junctions contribute to pathological permeability and tumorigenesis. |
| References |
|---|
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.