- Inhibitors
- Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
VEGFB Antibody [E11E24]
Cat.No.: F2353
Application:
Reactivity:
Experiment Essentials
WB
Recommended wet transfer conditions: 200 mA, 60 min.
Recommended wet transfer conditions: 200 mA, 60 min.
Usage Information
| Dilution |
|---|
|
| Application |
|---|
| WB |
| Reactivity |
|---|
| Rat, Mouse |
| Source |
|---|
| Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody |
| Storage Buffer |
|---|
| PBS, pH 7.2+50% Glycerol+0.05% BSA+0.01% NaN3 |
| Storage (from the date of receipt) |
|---|
| -20°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles), 2 years |
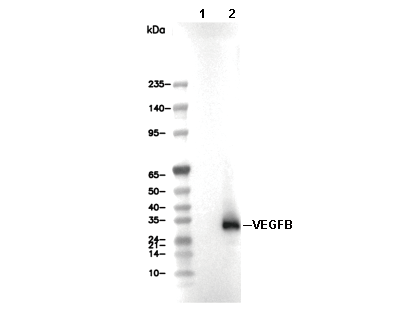
| Predicted MW Observed MW |
|---|
| 22 kDa 19 kDa |
| *Why do the predicted and actual molecular weights differ? The following reasons may explain differences between the predicted and actual protein molecular weight. |
Exprimental Methods
| WB |
|---|
Experimental Protocol:
Sample preparation
1. Tissue: Lyse the tissue sample by adding an appropriate volume of ice-cold RIPA/NP-40 Lysis Buffer (containing Protease Inhibitor Cocktail),and homogenize the tissue at a low temperature. 2. Adherent cell: Aspirate the culture medium and wash the cells with ice-cold PBS twice. Lyse the cells by adding an appropriate volume of RIPA/NP-40 Lysis Buffer (containing Protease Inhibitor Cocktail) and put the sample on ice for 5 min. 3. Suspension cell: Transfer the culture medium to a pre-cooled centrifuge tube. Centrifuge and aspirate the supernatant. Wash the cells with ice-cold PBS twice. Lyse the cells by adding an appropriate volume of RIPA/NP-40 Lysis Buffer (containing Protease Inhibitor Cocktail) and put the sample on ice for 5 min. 4. Place the lysate into a pre-cooled microcentrifuge tube. Centrifuge at 4°C for 15 min. Collect the supernatant;
5. Remove a small volume of lysate to determine the protein concentration;
6. Combine the lysate with protein loading buffer. Boil 20 µL sample under 95-100°C for 5 min. Centrifuge for 5 min after cool down on ice.
Electrophoretic separation
1. According to the concentration of extracted protein, load appropriate amount of protein sample and marker onto SDS-PAGE gels for electrophoresis. Recommended separating gel (lower gel) concentration: 10%. Reference Table for Selecting SDS-PAGE Separation Gel Concentrations 2. Power up 80V for 30 minutes. Then the power supply is adjusted (110 V~150 V), the Marker is observed, and the electrophoresis can be stopped when the indicator band of the predyed protein Marker where the protein is located is properly separated. (Note that the current should not be too large when electrophoresis, too large current (more than 150 mA) will cause the temperature to rise, affecting the result of running glue. If high currents cannot be avoided, an ice bath can be used to cool the bath.)
Transfer membrane
1. Take out the converter, soak the clip and consumables in the pre-cooled converter;
2. Activate PVDF membrane with methanol for 1 min and rinse with transfer buffer;
3. Install it in the order of "black edge of clip - sponge - filter paper - filter paper - glue -PVDF membrane - filter paper - filter paper - sponge - white edge of clip"; 4. The protein was electrotransferred to PVDF membrane. ( 0.45 µm PVDF membrane is recommended ) Reference Table for Selecting PVDF Membrane Pore Size Specifications Recommended conditions for wet transfer: 200 mA, 60 min. ( Note that the transfer conditions can be adjusted according to the protein size. For high-molecular-weight proteins, a higher current and longer transfer time are recommended. However, ensure that the transfer tank remains at a low temperature to prevent gel melting.)
Block
1. After electrotransfer, wash the film with TBST at room temperature for 5 minutes;
2. Incubate the film in the blocking solution for 1 hour at room temperature;
3. Wash the film with TBST for 3 times, 5 minutes each time.
Antibody incubation
1. Use 5% skim milk powder to prepare the primary antibody working liquid (recommended dilution ratio for primary antibody 1:1000), gently shake and incubate with the film at 4°C overnight; 2. Wash the film with TBST 3 times, 5 minutes each time;
3. Add the secondary antibody to the blocking solution and incubate with the film gently at room temperature for 1 hour;
4. After incubation, wash the film with TBST 3 times for 5 minutes each time.
Antibody staining
1. Add the prepared ECL luminescent substrate (or select other color developing substrate according to the second antibody) and mix evenly;
2. Incubate with the film for 1 minute, remove excess substrate (keep the film moist), wrap with plastic film, and expose in the imaging system. |
Biological Description
| Specificity |
|---|
| VEGFB Antibody [E11E24] detects endogenous levels of total VEGFB protein. |
| Subcellular Location |
|---|
| Secreted |
| Uniprot ID |
|---|
| P49765 |
| Clone |
|---|
| E11E24 |
| Synonym(s) |
|---|
| VRF; VEGFB; Vascular endothelial growth factor B; VEGF-B; VEGF-related factor |
| Background |
|---|
| Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor B (VEGFB) is a homodimeric cytokine belonging to the PDGF/VEGF family that promotes angiogenesis and regulates lipid metabolism in metabolically active tissues such as the heart, skeletal muscle, and brown adipose tissue. VEGFB exists as two isoforms, VEGFB167 (heparin-binding, matrix-associated) and VEGFB186 (secreted form), both featuring a conserved cystine-knot motif with six cysteine residues forming three disulfide bonds that stabilize the characteristic VEGF dimer structure essential for receptor binding. VEGFB binds with high affinity to VEGFR-1 (Flt-1) primarily through specific residues in its receptor-binding loops, activating signaling cascades that support endothelial cell survival and proliferation without strong mitogenic activity compared to VEGF-A. VEGFB enhances vascular permeability and stabilization while uniquely regulating fatty acid transport across endothelial barriers via induction of translocase proteins like CD36 and FABP4/5, thereby coordinating blood vessel formation with tissue energy demands. VEGFB signals through VEGFR-1 homodimers or VEGFR-1/VEGFR-2 heterodimers, activating PI3K/Akt and PLCγ pathways to promote vessel maturation rather than sprouting angiogenesis. Dysregulated VEGFB contributes to cardiovascular pathologies, including ischemic heart disease and atherosclerosis, acting as a therapeutic target for improving cardiac vascularization and metabolic homeostasis. |
| References |
|---|
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.