- Inhibitors
- Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
TRP2/DCT Antibody [K24G11]
Cat.No.: F3990
Application:
Reactivity:
Usage Information
| Dilution |
|---|
|
| Application |
|---|
| WB, IP, IHC |
| Reactivity |
|---|
| Mouse, Human |
| Source |
|---|
| Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody |
| Storage Buffer |
|---|
| PBS, pH 7.2+50% Glycerol+0.05% BSA+0.01% NaN3 |
| Storage (from the date of receipt) |
|---|
| -20°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles), 2 years |
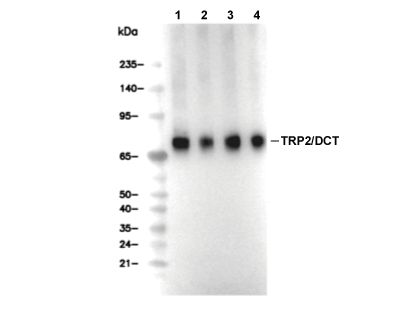
| Predicted MW Observed MW |
|---|
| 59 kDa 69 kDa,85 kDa |
| *Why do the predicted and actual molecular weights differ? The following reasons may explain differences between the predicted and actual protein molecular weight. |
| Positive Control | Human skin tissue; Human melanoma tissue; MeWo cells; SK-MEL-2 cells; SK-MEL-28 cells; F9 cells; B16-F0 cells |
|---|---|
| Negative Control |
Biological Description
| Specificity |
|---|
| TRP2/DCT Antibody [K24G11] detects endogenous levels of total TRP2/DCT protein. |
| Clone |
|---|
| K24G11 |
| Synonym(s) |
|---|
| TYRP2, DCT, L-dopachrome tautomerase, DT, L-dopachrome Delta-isomerase, Tyrosinase-related protein 2, TRP-2, TRP2 |
| Background |
|---|
| TRP2, also known as DCT (dopachrome tautomerase), is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein of the tyrosinase-related protein family, characterized by an N-terminal ectodomain containing a conserved metal-binding motif (HxH-x10-Hx2-H) critical for dopachrome isomerization, a single transmembrane helix that anchors it to melanosomal membranes, and a short C-terminal cytoplasmic tail that enables complex formation with tyrosinase (TYR) and TYRP1, stabilizing the melanogenic enzyme cluster essential for eumelanin synthesis. Predominantly expressed in melanocytes under the control of MITF, DCT catalyzes the stereospecific conversion of dopachrome to 5,6-dihydroxyindole-2-carboxylic acid (DHICA), steering melanin synthesis toward carboxylated black eumelanin instead of the more degradation-prone dihydroxyindole pathway, thereby enhancing photoprotection by scavenging reactive oxygen species, stabilizing melanin polymers, and protecting DNA from UV-induced damage, while also modulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling to influence melanocyte differentiation and survival. DCT integrates into maturing melanosomes, where TYR-generated dopachrome is processed through its active site for tautomerization, with TYRP1 further enhancing DCT’s stability and function; in melanoma, elevated DCT expression supports tumor progression by conferring anti-apoptotic properties and facilitating immune evasion as a recognized melanoma antigen, whereas mutations that impair DHICA production underlie pigmentary disorders such as oculocutaneous albinism and vitiligo, disrupting melanin homeostasis and increasing susceptibility to redox imbalance and pheomelanin accumulation. |
| References |
|---|
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.