- Inhibitors
- Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
TCF12/HEB Antibody [G2F21]
Cat.No.: F6098
Application:
Reactivity:
Usage Information
| Dilution |
|---|
|
| Application |
|---|
| WB, IP, IHC |
| Reactivity |
|---|
| Human |
| Source |
|---|
| Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody |
| Storage Buffer |
|---|
| PBS, pH 7.2+50% Glycerol+0.05% BSA+0.01% NaN3 |
| Storage (from the date of receipt) |
|---|
| -20°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles), 2 years |
| Predicted MW |
|---|
| 85 kDa |
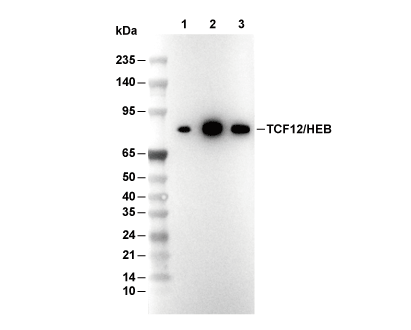
| Positive Control | Human esophageal carcinoma; Human colon adenocarcinoma; Human squamous cell carcinoma of the skin; Human prostate adenocarcinoma; Human lymph node; Human placenta; Human esophagus; IMR-32 cells; Jurkat cells; MLT-4 cells |
|---|---|
| Negative Control | MDA-MB-468 cells |
Biological Description
| Specificity |
|---|
| TCF12/HEB Antibody [G2F21] detects endogenous levels of total TCF12/HEB protein. |
| Clone |
|---|
| G2F21 |
| Synonym(s) |
|---|
| TCF12; Transcription factor 12; TCF-12; Class B basic helix-loop-helix protein 20 (bHLHb20); DNA-binding protein HTF4; E-box-binding protein; Transcription factor HTF-4; BHLHB20; HEB; HTF4 |
| Background |
|---|
| TCF12/HEB (Transcription Factor 12/HeLa E-box Binding protein) is a class I E-protein basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) transcription factor encoded by TCF12 at chromosome 15q21, existing in two major isoforms: HEBCan (681 amino acids, from the ubiquitous promoter) and HEBAlt (short form, from a distal promoter). These isoforms heterodimerize with tissue-specific bHLH partners such as E47, MyoD, and NeuroD via their conserved bHLH domain, which consists of a basic DNA-binding region and an HLH motif for dimerization, to recognize CANNTG E-box consensus sequences, thereby driving lineage commitment in T/B cells, muscle, and neurons. TCF12/HEB contains an N-terminal activation domain rich in acidic residues for coactivator recruitment, a central transactivation domain with glutamine/proline stretches that enhance RNA polymerase II pausing and release, the core bHLH domain (~60 residues) where the basic helix contacts the major groove of DNA while HLH amphipathic helices dimerize through hydrophobic interfaces, and C-terminal inhibitory domains that modulate partner specificity. Alternative splicing at exon 1 generates HEBCan for broad T cell developmental stages and HEBAlt, which is enriched in DN2/DN3 thymocytes to promote efficient precursor generation. TCF12/HEB orchestrates T cell development by co-binding Lmo2 and Lyl1 at Eβ and Cd4 enhancers to activate genes involved in recombination and expansion, represses E2A targets through competitive dimerization to limit self-renewal, and balances hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) reconstitution versus differentiation, with deficiency resulting in myeloid bias, B/T cell blockage, and proliferation defects. PKCθ/Carma1 signaling phosphorylates HEBCan at serine residues, relieving Id protein-mediated autoinhibition and enabling TCR-induced chromatin looping with Runx1 and Foxp1 for Il2ra and Dtx1 expression, while HEBAlt uniquely partners with Bcl11b at the Tcrα enhancer to facilitate positive selection. TCF12 mutations cause coronal craniosynostosis (Saethre-Chotzen syndrome) by disrupting Twist1 heterodimerization and suture patency; haploinsufficiency is linked to dyslexia through neurodevelopmental gene dysregulation, and somatic alterations contribute to leukemia (AML1-ETO fusions) or solid tumor progression via EMT and invasion. |
| References |
|---|
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.