- Inhibitors
- Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
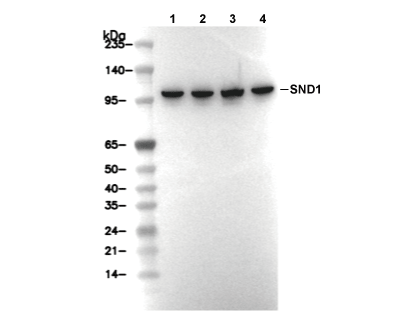
SND1 Antibody [J10N22]
Cat.No.: F5098
Application:
Reactivity:
Usage Information
| Dilution |
|---|
|
| Application |
|---|
| WB, IP, IHC, IF, ELISA |
| Reactivity |
|---|
| Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Source |
|---|
| Mouse Monoclonal Antibody |
| Storage Buffer |
|---|
| PBS, pH 7.2+50% Glycerol+0.05% BSA+0.01% NaN3 |
| Storage (from the date of receipt) |
|---|
| -20°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles), 2 years |
| Predicted MW Observed MW |
|---|
| 101 kDa 101 kDa |
| *Why do the predicted and actual molecular weights differ? The following reasons may explain differences between the predicted and actual protein molecular weight. |
| Positive Control | Human pancreas tissue; Human colon cancer tissue; HepG2 cells; HEK-293 cells; Jurkat cells; HSC-T6 cells; NIH/3T3 cells |
|---|---|
| Negative Control |
Biological Description
| Specificity |
|---|
| SND1 Antibody [J10N22] detects endogenous levels of total SND1 protein. |
| Clone |
|---|
| J10N22 |
| Synonym(s) |
|---|
| SND1; Staphylococcal nuclease domain-containing protein 1; EC:3.1.31.1; 100 kDa coactivator; EBNA2 coactivator p100; Tudor domain-containing protein 11; p100 co-activator; TDRD11 |
| Background |
|---|
| SND1 (Staphylococcal nuclease domain-containing 1, also known as Tudor-SN or p100) is a highly conserved 910-amino-acid protein encoded by the SND1 gene at chromosome 7q31.3, recognized for its dual roles as a nuclease and scaffolding factor in RNA metabolism, transcriptional coactivation, and cellular stress responses. SND1 contains an N-terminal tandem repeat of four staphylococcal nuclease (SN) domains (SN1–4) that confer double-stranded RNA endonuclease activity for mRNA degradation within the RISC complex, and a C-terminal region that fuses a Tudor domain, which recognizes methylated arginines and histone marks such as H4R3me, with a partial fifth SN-like domain for protein–nucleic acid interactions and U5 snRNA-dependent spliceosome assembly. SND1 acts as a transcriptional coactivator for factors like STAT5/6, c-Myc, and EBNA2 by recruiting histone acetyltransferases (GCN5) to methylated histones for chromatin relaxation, mediates degradation of miRNA-targeted mRNAs in RISC to silence gene expression, and promotes alternative splicing of pro-invasive isoforms such as CD44v6. Upon DNA damage, SND1 is recruited by PARP1 to chromatin, where it collaborates with ALC1 and GCN5 to facilitate chromatin remodeling and repair. The SN domains hydrolyze phosphodiester bonds in dsRNA, while the Tudor-SN region senses epigenetic marks to amplify regulatory signals, and SN activity can be competitively inhibited by pdTp. SND1 overexpression drives angiogenesis by upregulating VEGF in HCC xenografts, enhances metastasis through modulation of CD44 splicing and PPARγ-mediated lipid metabolism, and is associated with poor prognosis by supporting cancer cell proliferation and invasion. |
| References |
|---|
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.