- Inhibitors
- Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
SMURF 2 Antibody [A20L4]
Cat.No.: F4819
Application:
Reactivity:
Usage Information
| Dilution |
|---|
|
| Application |
|---|
| WB |
| Reactivity |
|---|
| Human |
| Source |
|---|
| Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody |
| Storage Buffer |
|---|
| PBS, pH 7.2+50% Glycerol+0.05% BSA+0.01% NaN3 |
| Storage (from the date of receipt) |
|---|
| -20°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles), 2 years |
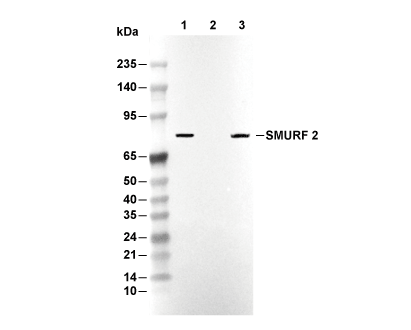
| Predicted MW Observed MW |
|---|
| 86 kDa 86 kDa |
| *Why do the predicted and actual molecular weights differ? The following reasons may explain differences between the predicted and actual protein molecular weight. |
| Positive Control | HeLa cells; U-2 OS cells; SH-SY-5Y cells |
|---|---|
| Negative Control |
Biological Description
| Specificity |
|---|
| SMURF 2 Antibody [A20L4] detects endogenous levels of total SMURF 2 protein. |
| Clone |
|---|
| A20L4 |
| Synonym(s) |
|---|
| E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase SMURF2; hSMURF2; HECT-type E3 ubiquitin transferase SMURF2; SMAD ubiquitination regulatory factor 2; SMAD-specific E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase 2; SMURF2 |
| Background |
|---|
| Smurf2 (Smad ubiquitin regulatory factor 2) is a member of the NEDD4 family of HECT-type E3 ubiquitin ligases. It plays a pivotal role in negatively regulating TGF-β/BMP signaling pathways and helping maintain cellular homeostasis through targeted protein degradation. Smurf2 features an N-terminal C2 domain, which mediates membrane association and autoinhibition by binding to its own HECT domain. The central region contains three WW domains that recognize PPXY motifs on substrates or adaptor proteins, such as Smad7. Its C-terminal HECT catalytic domain possesses an active-site cysteine (Cys716) crucial for ubiquitin transfer, and this domain remains autoinhibited until activated by adaptor binding or phosphorylation. Smurf2 partners with Smad7 to target TGF-β type I receptors and receptor-regulated Smads (Smad1, Smad2, and Smad3) for ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation, effectively suppressing TGF-β/BMP signaling. Smurf2 also regulates the stability of other proteins, including RUNX2, ID2, EZH2, RNF20, and Topo IIα, influencing processes such as osteogenesis, cellular senescence, genomic stability, and cell cycle arrest. The role of Smurf2 in cancer is context-dependent: it can act as a tumor suppressor (through RNF20-mediated H2Bub1 regulation) or promote tumorigenesis (by enhancing migration in colorectal cancer). |
| References |
|---|
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.