- Inhibitors
- Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
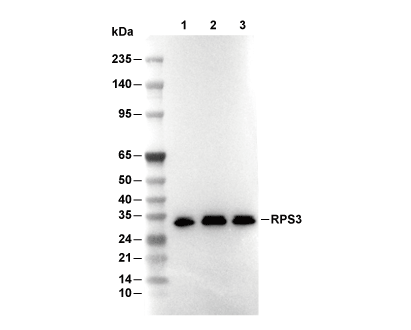
RPS3 (Ribosome Marker) Antibody [J10K2]
Cat.No.: F4881
Application:
Reactivity:
Usage Information
| Dilution |
|---|
|
| Application |
|---|
| WB, IHC, IF |
| Reactivity |
|---|
| Mouse, Rat, Human |
| Source |
|---|
| Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody |
| Storage Buffer |
|---|
| PBS, pH 7.2+50% Glycerol+0.05% BSA+0.01% NaN3 |
| Storage (from the date of receipt) |
|---|
| -20°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles), 2 years |
| Predicted MW |
|---|
| 27 kDa |
| Positive Control | Human kidney; Neuro-2a cells; HepG2 cells; PC-12 cells |
|---|---|
| Negative Control |
Biological Description
| Specificity |
|---|
| RPS3 (Ribosome Marker) Antibody [J10K2] detects endogenous levels of total RPS3 (Ribosome Marker) protein. |
| Clone |
|---|
| J10K2 |
| Synonym(s) |
|---|
| OK/SW-cl.26; RPS3; Small ribosomal subunit protein uS3; 40S ribosomal protein S3 |
| Background |
|---|
| RPS3 (ribosomal protein S3) is a multifunctional protein integral to the eukaryotic 40S ribosomal subunit, where it ensures accurate mRNA decoding and translation elongation through a dual-domain fold comprising an N-terminal RNA recognition motif that binds 18S rRNA for decoding center fidelity and a C-terminal globular domain that stabilizes rRNA and mediates extra-ribosomal interactions. In addition to its essential role in ribosome biogenesis and assembly with other ribosomal proteins such as RPS19 and RPS20, RPS3 also participates in extraribosomal functions, most notably in the DNA damage response. Upon genotoxic stress, RPS3 translocates to the nucleus, where phosphorylation at specific threonine residues enhances its interaction with base excision repair enzymes, promoting efficient removal of damaged bases, while concurrently suppressing non-homologous end joining by inhibiting DNA-PKcs and Lig4. RPS3 also partners with NF-κB, guiding the p65 subunit to select promoter sites and amplifying pro-inflammatory gene expression during immune responses and viral infections. RPS3 is aberrantly glycosylated and secreted, acting as an autocrine survival factor that facilitates metastasis and resistance to therapies such as proteasome inhibitors by activating pro-survival pathways like canonical NF-κB and disrupting negative regulators of p53. Dysregulation of RPS3 is linked to enhanced tumor invasion, poor prognosis, and increased resistance to chemoradiation, while its knockdown induces p53-dependent apoptosis and synergizes with DNA repair and proteasome inhibitors. |
| References |
|---|
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.