- Inhibitors
- Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
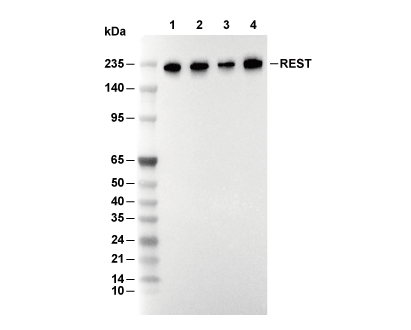
REST Antibody [G10D4]
Cat.No.: F4637
Application:
Reactivity:
Usage Information
| Dilution |
|---|
|
| Application |
|---|
| WB, ChIP |
| Reactivity |
|---|
| Human, Mouse, Rat, Monkey |
| Source |
|---|
| Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody |
| Storage Buffer |
|---|
| PBS, pH 7.2+50% Glycerol+0.05% BSA+0.01% NaN3 |
| Storage (from the date of receipt) |
|---|
| -20°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles), 2 years |
| Predicted MW |
|---|
| 200 kDa |
| Positive Control | HeLa cells; NIH/3T3 cells; C6 cells; COS-7 cells |
|---|---|
| Negative Control |
Biological Description
| Specificity |
|---|
| REST Antibody [G10D4] detects endogenous levels of total REST protein. |
| Clone |
|---|
| G10D4 |
| Synonym(s) |
|---|
| RE1-silencing transcription factor; Neural-restrictive silencer factor; X2 box repressor; REST; NRSF; XBR |
| Background |
|---|
| REST (RE1-silencing transcription factor), also known as NRSF, functions as a master transcriptional repressor that silences neuronal differentiation genes in non-neuronal cells and stem cells by binding neuron-restrictive silencer elements (NRSE/RE1) through its central zinc-finger DNA-binding domain comprising eight C2H2 tandem zinc fingers that recognize a 21-bp core motif (CACCCNNGGCAG) in an anti-parallel configuration with conformational flexibility, flanked by N-terminal RD1 and C-terminal RD2 repression domains plus lysine/proline-rich regions that recruit the CoREST complex (LSD1, HDAC1/2, Sin3A, MeCP2) for epigenetic silencing, alongside a lysine-rich NLS for nuclear localization. REST/CoREST nucleates local chromatin compaction via H3K9/27 methylation, nucleosome phasing shifts, and long-range looping to block enhancer-promoter contacts (inhibiting PCDHα HS5-1 enhancer via CTCF displacement), while regulating miRNA biogenesis (pri-miR processing via Drosha/DGCR8) and lncRNAs in feedback loops that maintain neural progenitor self-renewal; REST degradation during differentiation, via GSK3β phosphorylation and SCF-βTrCP ubiquitination, derepresses >2000 neuronal targets, including synaptophysin, β-III tubulin, and Nav channels, to enable neurogenesis. REST hyperactivation drives medulloblastoma, neuroblastoma, and Wilms tumor progression by enforcing stemness and blocking differentiation, while nuclear loss in Alzheimer's (via pathology-induced degradation) impairs neuroprotection and memory consolidation; REST polymorphisms associate with Huntington's chorea onset and schizophrenia susceptibility through dysregulated neuronal gene networks. |
| References |
|---|
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.