- Inhibitors
- Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
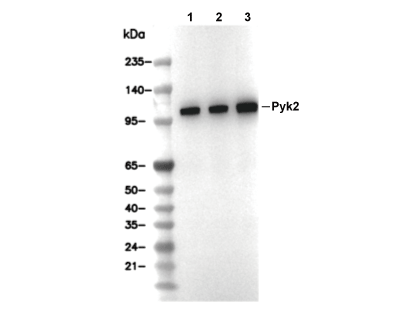
Pyk2 Antibody [L19B9]
Cat.No.: F4657
Application:
Reactivity:
Usage Information
| Dilution |
|---|
|
| Application |
|---|
| WB, IP |
| Reactivity |
|---|
| Human, Mouse |
| Source |
|---|
| Mouse Monoclonal Antibody |
| Storage Buffer |
|---|
| PBS, pH 7.2+50% Glycerol+0.05% BSA+0.01% NaN3 |
| Storage (from the date of receipt) |
|---|
| -20°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles), 2 years |
| Predicted MW |
|---|
| 116 kDa |
| Positive Control | Jurkat cells; Ramos cells; Raji cells |
|---|---|
| Negative Control |
Biological Description
| Specificity |
|---|
| Pyk2 Antibody [L19B9] detects endogenous levels of total Pyk2 protein. |
| Clone |
|---|
| L19B9 |
| Synonym(s) |
|---|
| Protein-tyrosine kinase 2-beta; Calcium-dependent tyrosine kinase (CADTK); CAK-beta; CAKB; Focal adhesion kinase 2 (FADK 2); Proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2; Related adhesion focal tyrosine kinase (RAFTK); PTK2B; FAK2; PYK2; RAFTK |
| Background |
|---|
| Pyk2 (proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2) is a non-receptor tyrosine kinase closely related to FAK, highly expressed in hematopoietic cells and neurons. It comprises an N-terminal FERM domain that regulates autoinhibition and oligomerization, a central bilobal kinase domain with key autophosphorylation sites at Tyr402 (activation loop) and Tyr579/580 (regulatory tyrosines), proline-rich regions (PR1/PR2) for SH3-domain interactions, and a C-terminal focal adhesion targeting (FAT) four-helix bundle domain that binds paxillin LD motifs to localize at cell adhesions. Activation is triggered by Ca2+ influx or integrin/GPCR engagement, which relieves FERM autoinhibition and enables Tyr402 autophosphorylation, leading to Src recruitment and subsequent phosphorylation of Tyr579/580. This initiates downstream signaling through pathways such as p130Cas-Crk-DOCK180-Rac1/CDC42 for cytoskeletal remodeling and migration, Grb2-SOS-Ras-ERK1/2 for gene expression and proliferation, and PI3K-AKT for survival, while FAT-paxillin scaffolding amplifies focal adhesion turnover essential for chemotaxis in macrophages/neutrophils and synaptic plasticity in neurons. Negative regulation occurs via calpain-mediated cleavage or PP2 phosphatases. Dysregulated Pyk2 activity drives osteoclast hyperactivity in arthritis by enhancing migration and invasion, neuronal excitotoxicity in epilepsy and stroke through Ca2+-dependent overactivation, and cancer metastasis (breast, prostate, glioblastoma) by promoting invadopodia formation and anoikis resistance. |
| References |
|---|
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.