- Inhibitors
- Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
POLDIP2 Antibody [N1K14]
Cat.No.: F3409
Application:
Reactivity:
Usage Information
| Dilution |
|---|
|
| Application |
|---|
| WB, IP, IF |
| Reactivity |
|---|
| Human |
| Source |
|---|
| Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody |
| Storage Buffer |
|---|
| PBS, pH 7.2+50% Glycerol+0.05% BSA+0.01% NaN3 |
| Storage (from the date of receipt) |
|---|
| -20°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles), 2 years |
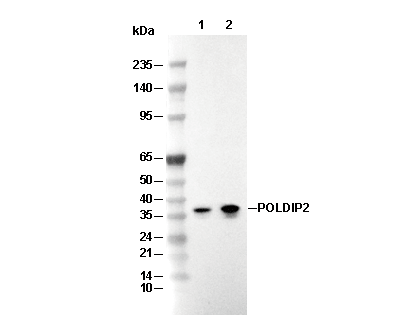
| Predicted MW Observed MW |
|---|
| 42 kDa 38 kDa, 37 kDa |
| *Why do the predicted and actual molecular weights differ? The following reasons may explain differences between the predicted and actual protein molecular weight. |
| Positive Control | HAP1 cells; HeLa cells; HepG2 cells |
|---|---|
| Negative Control |
Biological Description
| Specificity |
|---|
| POLDIP2 Antibody [N1K14] detects endogenous levels of total POLDIP2 protein. |
| Clone |
|---|
| N1K14 |
| Synonym(s) |
|---|
| PDIP38; POLDIP2; Polymerase delta-interacting protein 2; 38 kDa DNA polymerase delta interaction protein; p38 |
| Background |
|---|
| POLDIP2 (polymerase δ-interacting protein 2) is a multifunctional protein most abundantly expressed in heart and skeletal muscle, characterized by a compact two-domain β-strand-rich globular structure with an N-terminal dynamic unstructured region tethered by an extended linker to a rigid core comprising a YccV-like domain and a juxtaposed DUF525 domain that together form a central channel. Its inter-strand loops provide conformational flexibility, facilitating interactions with various partner proteins. POLDIP2 functions as an essential cofactor for DNA polymerase δ, enhancing replication fork stability through interaction with PCNA and stimulating PrimPol processivity and error-free bypass of oxidative DNA lesions by binding to the catalytic domain. It also supports genomic integrity by coordinating base excision repair and homologous recombination in conjunction with RAD51. POLDIP2 dynamically regulates Nox4/p22^phox-mediated reactive oxygen species production, which is critical for focal adhesion turnover and cytoskeletal remodeling during vascular smooth muscle cell migration. POLDIP2 controls the lipoylation of PDH and αKGDH complexes by inhibiting Clp-protease-mediated ACSM1 degradation under hypoxic conditions regulated by HIF-1α, thereby preserving oxidative metabolism. Loss of POLDIP2 results in mitochondrial dysfunction and retrograde metabolic reprogramming, while its overexpression contributes to diabetic retinopathy inflammation through Pink1 degradation and inhibition of mitophagy. Dysregulation of POLDIP2 has also been implicated in promoting cancer cell proliferation, cardiovascular diseases through endothelial Nox4 hyperactivation, and pathological neovascularization via effects on the cytoskeleton. |
| References |
|---|
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.