- Inhibitors
- Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
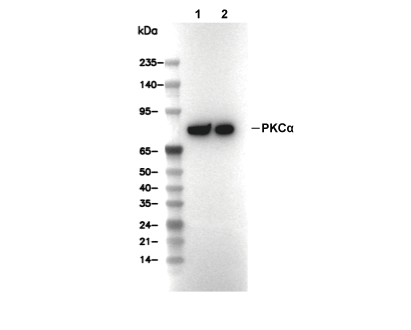
PKCα Antibody [B21A18]
Cat.No.: F6058
Application:
Reactivity:
Usage Information
| Dilution |
|---|
|
| Application |
|---|
| WB, IF, FCM |
| Reactivity |
|---|
| Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Source |
|---|
| Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody |
| Storage Buffer |
|---|
| PBS, pH 7.2+50% Glycerol+0.05% BSA+0.01% NaN3 |
| Storage (from the date of receipt) |
|---|
| -20°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles), 2 years |
| Predicted MW |
|---|
| 80 kDa |
| Positive Control | SH-SY5Y cells; NIH/3T3 cells; SK-N-SH cells (TPA, 200 nM, 30 min) |
|---|---|
| Negative Control | SK-MEL-2 cells |
Biological Description
| Specificity |
|---|
| PKCα Antibody [B21A18] detects endogenous levels of total PKCα protein. |
| Clone |
|---|
| B21A18 |
| Synonym(s) |
|---|
| PRKCA; Protein kinase C alpha type; EC:2.7.11.13; PKC-A; PKC-alpha; PKCA; PRKACA |
| Background |
|---|
| PKCα (protein kinase C alpha) is a classical, calcium-dependent serine/threonine kinase that plays a pivotal role in transducing signals for diverse cellular responses, including gene expression, secretion, proliferation, and muscle contraction. As a member of the PKC family, PKCα is activated by the coordinated binding of calcium ions to its C2 domain and phosphatidylserine and diacylglycerol (DAG) to its cysteine-rich C1 domain, with phorbol esters serving as potent pharmacological activators. The protein features an autoinhibitory pseudosubstrate domain that occupies the substrate-binding pocket of the catalytic domain, maintaining PKCα in an inactive conformation until cofactor or activator binding induces a conformational change. Full activation requires a series of phosphorylation events, notably at threonine and serine residues within the activation loop (Thr500), turn motif (Thr641), and hydrophobic motif (Ser660), often mediated by PDK1 and autophosphorylation, which stabilize the active conformation and promote downstream signaling. PKCα translocates to the plasma membrane upon activation, where it phosphorylates a wide spectrum of substrates involved in cytoskeletal remodeling, ion channel regulation, and transcriptional control, thus integrating extracellular cues into precise cellular outcomes. Dysregulation of PKCα activity has been implicated in cardiovascular disease, cancer progression, and neurological disorders. |
| References |
|---|
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.