- Inhibitors
- Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
PI 3 Kinase catalytic subunit α/PIK3CA Antibody [C16C18]
Cat.No.: F4899
Application:
Reactivity:
Usage Information
| Dilution |
|---|
|
| Application |
|---|
| WB, IP, IF, FCM |
| Reactivity |
|---|
| Mouse, Rat, Human |
| Source |
|---|
| Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody |
| Storage Buffer |
|---|
| PBS, pH 7.2+50% Glycerol+0.05% BSA+0.01% NaN3 |
| Storage (from the date of receipt) |
|---|
| -20°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles), 2 years |
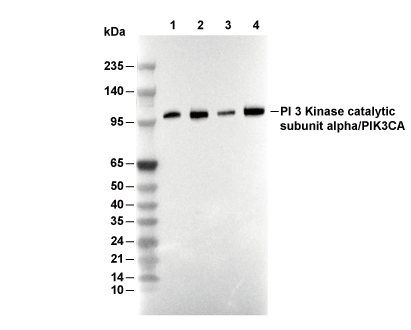
| Predicted MW Observed MW |
|---|
| 124 kDa 110 kDa, 120 kDa |
| *Why do the predicted and actual molecular weights differ? The following reasons may explain differences between the predicted and actual protein molecular weight. |
| Positive Control | Rat Brain Tissue; Mouse Brain Tissue; Jurkat cells; HAP1 cells; Raw264.7 cells; HeLa cells; NIH/3T3 cells; MCF-7 cells |
|---|---|
| Negative Control |
Biological Description
| Specificity |
|---|
| PI 3 Kinase catalytic subunit α/PIK3CA Antibody [C16C18] detects endogenous levels of total PI 3 Kinase catalytic subunit α/PIK3CA protein. |
| Clone |
|---|
| C16C18 |
| Synonym(s) |
|---|
| PI3-kinase subunit alpha; PI3K-alpha; PI3Kalpha; Serine/threonine protein kinase PIK3CA; PtdIns-3-kinase subunit p110-alpha; p110alpha; PIK3CA |
| Background |
|---|
| PIK3CA (phosphoinositide 3-kinase catalytic subunit α, p110α) is the class I PI3Kα catalytic isoform that is ubiquitously expressed and transduces growth factor and receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) signals into PIP3 second messengers, driving cellular proliferation, survival, and metabolism. It forms a heterodimer with p85α or p85β regulatory subunits through a five-domain architecture that includes an N-terminal ABD domain docking p85 via specific contacts, a Ras-binding domain engaging Ras-GTP, a C2 domain containing a membrane-inserting basic pocket, a helical domain with an inhibitory p85 interface, and a C-terminal kinase domain with a bilobal fold, ATP-binding hinge, catalytic loop, activation loop, and a regulatory arch for substrate positioning. Activation occurs when RTK-mediated phosphorylation of p85 relieves autoinhibition, allowing membrane recruitment and phosphorylation of PIP2 to generate PIP3, which recruits Akt and facilitates its phosphorylation by PDK1 and TORC2, propagating downstream signaling. Oncogenic mutations such as E542K and E545K in the helical domain disrupt p85 inhibition, H1047R in the kinase domain rigidifies the activation loop, and N345K or R88Q in the ABD or RBD increase Ras or membrane affinity, leading to hyperactivation of PI3K/AKT/mTORC1 pathways. This hyperactivation promotes translation, inhibits pro-apoptotic factors, and blocks apoptosis in a significant proportion of breast, colorectal, and endometrial tumors, while other mutations are linked to vascular malformations. |
| References |
|---|
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.