- Inhibitors
- Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
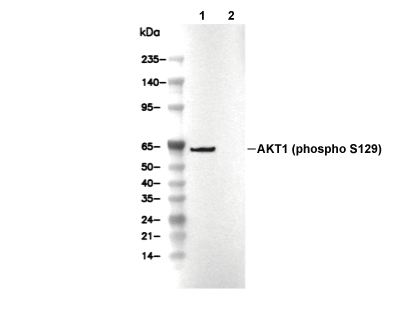
Phospho-Akt1 (Ser129) Antibody [K23C4]
Cat.No.: F4918
Application:
Reactivity:
Usage Information
| Dilution |
|---|
|
| Application |
|---|
| WB |
| Reactivity |
|---|
| Human |
| Source |
|---|
| Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody |
| Storage Buffer |
|---|
| PBS, pH 7.2+50% Glycerol+0.05% BSA+0.01% NaN3 |
| Storage (from the date of receipt) |
|---|
| -20°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles), 2 years |
| Predicted MW |
|---|
| 55 kDa |
| Positive Control | MCF-7 cells |
|---|---|
| Negative Control |
Biological Description
| Specificity |
|---|
| Phospho-Akt1 (Ser129) Antibody [K23C4] detects endogenous levels of total Akt1 protein only when it is phosphorylated at Ser129. |
| Clone |
|---|
| K23C4 |
| Synonym(s) |
|---|
| PKB; RAC; AKT1; RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase; Protein kinase B; Protein kinase B alpha; Proto-oncogene c-Akt; RAC-PK-alpha; PKB alpha |
| Background |
|---|
| Phospho-Akt1 (Ser129) is a specific post-translational modification of Akt1 (RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase, PKBα), occurring within the flexible linker region between the pleckstrin homology (PH) domain and the kinase domain of this 480-amino-acid protein. Akt1 comprises an N-terminal PH domain for PIP3-mediated membrane recruitment, a catalytic kinase domain with key regulatory phosphorylation sites at Thr308 (activation loop) and Ser473 (hydrophobic motif), and a C-terminal regulatory tail. Phosphorylation of Ser129 by protein kinase CK2 generates a consensus S-x-x-D/E motif that primes subsequent modification at Ser126 and stabilizes the overall conformation of Akt1. This modification hyperactivates Akt1 beyond the effects of canonical PDK1/mTORC2 phosphorylation by strengthening its association with the HSP90 chaperone complex, which protects Thr308 from PP2A-mediated dephosphorylation, thereby sustaining Akt1 kinase activity. Additionally, phospho-Ser129 enhances β-catenin/TCF transcriptional activity, either directly or by stabilizing Wnt signaling components, and locks Akt1 in an extended active conformation that allows for isoform-specific substrate selection, such as preferential phosphorylation of palladin, a process not mirrored in Akt2 due to the absence of the equivalent Ser131 site. This modification drives cytoskeletal remodeling, cell survival through inhibition of Bad and FoxO, proliferation by promoting cyclin D1 stability and p27/p21 sequestration, and mTORC1 activation via TSC2 phosphorylation, with hierarchical phosphorylation ensuring robust signal amplification upon growth factor stimulation. In disease, elevated phospho-Ser129 levels enhance cancer cell survival and metastasis by amplifying PI3K/Akt oncogenic signaling (notably in breast and prostate cancers), contribute to chemoresistance via sustained HSP90 protection, and are implicated in metabolic disorders through disruption of glucose homeostasis by hyperactiving Akt1. |
| References |
|---|
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.