- Inhibitors
- Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
p47phox Antibody [L8D20]
Cat.No.: F4804
Application:
Reactivity:
Usage Information
| Dilution |
|---|
|
| Application |
|---|
| WB, IP, IHC |
| Reactivity |
|---|
| Human |
| Source |
|---|
| Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody |
| Storage Buffer |
|---|
| PBS, pH 7.2+50% Glycerol+0.05% BSA+0.01% NaN3 |
| Storage (from the date of receipt) |
|---|
| -20°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles), 2 years |
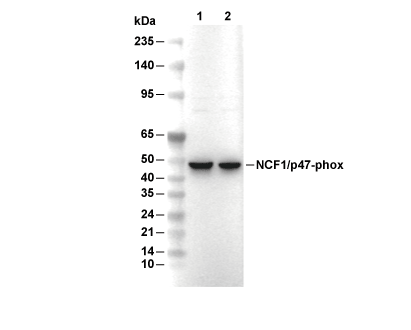
| Predicted MW Observed MW |
|---|
| 44 kDa 45 kDa |
| *Why do the predicted and actual molecular weights differ? The following reasons may explain differences between the predicted and actual protein molecular weight. |
| Positive Control | Human spleen tissue; Raji cells; Ramos cells |
|---|---|
| Negative Control |
Biological Description
| Specificity |
|---|
| p47phox Antibody [L8D20] detects endogenous levels of total p47phox protein. |
| Clone |
|---|
| L8D20 |
| Synonym(s) |
|---|
| NOXO2; SH3PXD1A; NCF1; Neutrophil cytosol factor 1; NCF-1; 47 kDa neutrophil oxidase factor; NCF-47K; Neutrophil NADPH oxidase factor 1; Nox organizer 2; Nox-organizing protein 2; SH3 and PX domain-containing protein 1A; p47-phox |
| Background |
|---|
| p47phox (neutrophil cytosolic factor 1, NCF1) is a critical organizer subunit of the phagocyte NADPH oxidase 2 (NOX2) complex, which is essential for innate immunity by coordinating the assembly of cytosolic factors (p47phox, p67phox, p40phox, Rac) with the membrane-bound cytochrome b558 (gp91phox/NOX2-p22phox) to facilitate superoxide production for microbial killing; its deficiency leads to chronic granulomatous disease (CGD), characterized by recurrent infections. The 390-amino-acid p47phox protein adopts an autoinhibited conformation, featuring an N-terminal phox homology (PX) domain that binds PI(3,4)P2 or phosphatidic acid for membrane targeting, tandem Src homology 3 (SH3) domains that, in the resting state, interact with an autoinhibitory region (AIR) to block activity, a C-terminal proline-rich region (PRR), and a serine-rich tail (Ser303–Ser379) containing multiple phosphorylation sites as well as polybasic motifs for initial p22phox docking. Upon pathogen recognition, rapid and multi-site phosphorylation by kinases such as PKC, MAPK, and PAK at C-terminal serines (notably Ser303/304/328/359/370) disrupts the AIR-SH3 interaction, exposes cryptic SH3 domains to engage the p22phox PRR for membrane translocation, releases the PX domain for lipid docking, and recruits p67phox and Rac to activate the flavocytochrome for electron transfer from NADPH to O₂, producing superoxide via ping-pong kinetics. This phosphorylation-driven conformational switch ensures spatial and temporal control of ROS generation at phagosomes, with mutations like Δ219–222 or W193R in p47phox impairing SH3-p22phox binding and reducing superoxide output by 60–100%. Post-translational modifications, such as Tyr159/240 phosphorylation, further enhance oxidase priming. Dysregulated p47phox activity contributes to vascular oxidative stress in hypertension and heart failure through endothelial NOX activation, promotes atherosclerosis via ROS generated by vascular smooth muscle cells and monocytes, and is implicated in inflammatory diseases where NOX2 hyperactivity leads to tissue damage. |
| References |
|---|
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.