- Inhibitors
- Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
P cadherin Antibody [B17B8]
Cat.No.: F4829
Application:
Reactivity:
Usage Information
| Dilution |
|---|
|
| Application |
|---|
| WB, IHC, IF |
| Reactivity |
|---|
| Human |
| Source |
|---|
| Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody |
| Storage Buffer |
|---|
| PBS, pH 7.2+50% Glycerol+0.05% BSA+0.01% NaN3 |
| Storage (from the date of receipt) |
|---|
| -20°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles), 2 years |
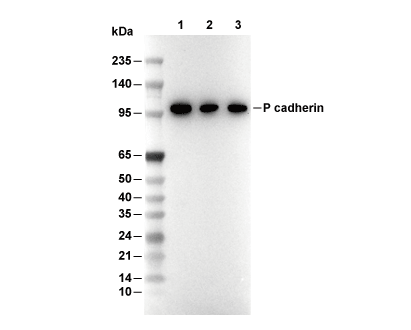
| Predicted MW Observed MW |
|---|
| 91 kDa 120 kDa |
| *Why do the predicted and actual molecular weights differ? The following reasons may explain differences between the predicted and actual protein molecular weight. |
| Positive Control | Human breast cancer tissue; Human breast tissue; BxPC-3 cells; A431 cells; PC-3 cells |
|---|---|
| Negative Control |
Biological Description
| Specificity |
|---|
| P cadherin Antibody [B17B8] detects endogenous levels of total P cadherin protein. |
| Clone |
|---|
| B17B8 |
| Synonym(s) |
|---|
| CDHP, CDH3, Cadherin-3, Placental cadherin, P-cadherin |
| Background |
|---|
| P-cadherin (CDH3) is a classical calcium-dependent transmembrane glycoprotein of the cadherin superfamily that mediates homophilic cell-cell adhesion, playing essential roles in placental trophoblast invasion, mammary gland development, and maintenance of epithelial integrity. Its extracellular domain is composed of five tandem EC repeats with calcium-binding linkers that rigidify the ectodomain, facilitating trans strand-swap dimerization at the EC1 domain via a conserved Trp2 interface. Anchored by a single transmembrane helix, P-cadherin’s cytoplasmic tail contains binding sites for β-catenin, α-catenin, and p120-catenin, establishing a complex that links adherens junctions to the actin cytoskeleton for junctional stability and efficient force transmission. P-cadherin localizes to basolateral adherens junctions and works in concert with E-cadherin to suppress invasive behavior by sequestering β-catenin and inhibiting canonical Wnt signaling. However, during epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), selective upregulation of P-cadherin, often accompanied by E-cadherin loss, promotes collective cell migration and branching morphogenesis through RhoA/ROCK-driven actomyosin contractility and matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) activation. P-cadherin overexpression is associated with poor prognosis in breast, ovarian, and gastric cancers, enhancing tumor cell motility, invasiveness, and metastasis, in part via PI3K/Akt-mediated survival signaling that operates independently of catenin binding. |
| References |
|---|
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.