- Inhibitors
- Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
NUR77 Antibody [J10J24]
Cat.No.: F4786
Application:
Reactivity:
Usage Information
| Dilution |
|---|
|
| Application |
|---|
| WB, IP, FCM |
| Reactivity |
|---|
| Human |
| Source |
|---|
| Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody |
| Storage Buffer |
|---|
| PBS, pH 7.2+50% Glycerol+0.05% BSA+0.01% NaN3 |
| Storage (from the date of receipt) |
|---|
| -20°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles), 2 years |
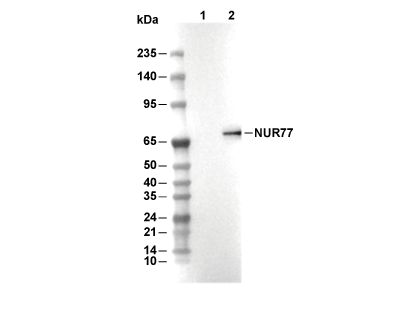
| Predicted MW Observed MW |
|---|
| 64 kDa 32 kDa,38 kDa,60-80 kDa |
| *Why do the predicted and actual molecular weights differ? The following reasons may explain differences between the predicted and actual protein molecular weight. |
| Positive Control | Jurkat cells (TPA, 40nM; A-23187, 2uM, 4 h); Jurkat cells (TPA, 40nM, A-23187, 2uM; MG-132, 10uM, 4 h); HeLa cells (MG-132, 10uM, 6h) |
|---|---|
| Negative Control | HeLa cells; Jurkat cells |
Biological Description
| Specificity |
|---|
| NUR77 Antibody [J10J24] detects endogenous levels of total NUR77 protein. |
| Clone |
|---|
| J10J24 |
| Synonym(s) |
|---|
| GFRP1; HMR; NAK1; NR4A1; Nuclear receptor subfamily 4 group A member 1; Early response protein NAK1; Nuclear hormone receptor NUR/77; Orphan nuclear receptor HMR; Orphan nuclear receptor TR3; ST-59; Testicular receptor 3; Nur77 |
| Background |
|---|
| NUR77 (NR4A1, TR3, NGFI-B) is an orphan nuclear receptor and immediate-early gene product that acts as a ligand-independent transcription factor rapidly induced by stress, growth factors, and apoptotic signals to regulate cell fate decisions in immunity, metabolism, and tumorigenesis. NUR77 has a canonical nuclear receptor architecture with an intrinsically disordered N-terminal A/B transactivation domain (AF-1) rich in phosphorylation sites, a central C-domain DNA-binding domain containing two zinc-finger motifs that recognize NBRE (AAAGGTCA) elements as a monomer or DR5 sites as RXR heterodimers, a flexible D-hinge region with nuclear localization signals, and a C-terminal E/F ligand-binding domain (aa 351–598) that lacks a classical hydrophobic pocket but supports AF-2 coactivator recruitment and homo/heterodimerization. Mechanistically, various kinases (ERK, JNK, PKC) phosphorylate the N-terminal domain to enhance transactivation and promote mitochondrial translocation, where NUR77 exposes a BH3-like motif to convert anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 into a pro-apoptotic conformer that releases cytochrome c and activates caspases. In the nucleus, NUR77 upregulates FasL, TRAIL, and TRAIL receptor expression to amplify extrinsic apoptosis, inhibits NF-κB p65 via direct interaction to suppress inflammation, and coactivates SREBP or PPARγ to balance lipogenesis and β-oxidation in metabolic tissues, while TCR-induced NUR77 enforces T-cell negative selection by sensitizing thymocytes to Bim-mediated apoptosis. NUR77 deficiency accelerates atherosclerosis through unchecked NF-κB-driven inflammation and foam cell formation, promotes autoimmunity by impairing T-cell apoptosis, and enhances chemical hepatocarcinogenesis. Overexpression or ligand activation suppresses tumor growth in prostate, lung, and ovarian cancers by restoring apoptosis. |
| References |
|---|
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.