- Inhibitors
- Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
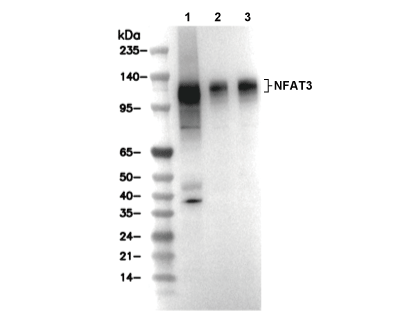
NFAT3 Antibody [H15F22]
Cat.No.: F4697
Application:
Reactivity:
Usage Information
| Dilution |
|---|
|
| Application |
|---|
| WB |
| Reactivity |
|---|
| Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Source |
|---|
| Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody |
| Storage Buffer |
|---|
| PBS, pH 7.2+50% Glycerol+0.05% BSA+0.01% NaN3 |
| Storage (from the date of receipt) |
|---|
| -20°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles), 2 years |
| Predicted MW |
|---|
| 120-140 kDa |
| Positive Control | A204 cells; A10 cells; HeLa cells |
|---|---|
| Negative Control |
Biological Description
| Specificity |
|---|
| NFAT3 Antibody [H15F22] detects endogenous levels of total NFAT3 protein. |
| Clone |
|---|
| H15F22 |
| Synonym(s) |
|---|
| Nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic 4; NF-ATc4; NFATc4; T-cell transcription factor NFAT3; NFATC4; NFAT3 |
| Background |
|---|
| NFAT3 (NFATc4), a nuclear factor of activated T-cells (NFAT) family transcription factor predominantly expressed in T cells, B cells, and cardiac myocytes, contains an intrinsically disordered N-terminal regulatory domain with serine-rich regions (SRR) and SP-repeat motifs that serve as calcineurin docking sites, a central Rel homology region (RHR) immunoglobulin-like fold with a DNA-binding domain recognizing GGAAA consensus sequences and a nuclear localization signal (NLS), and a C-terminal transactivation domain (TAD) that recruits CBP/p300 coactivators. Upon T cell receptor (TCR) or GPCR stimulation, increased cytosolic Ca2+ activates calmodulin-bound calcineurin, which dephosphorylates 14 conserved serine residues in the SRR/SP regions, exposing the NLS and enabling nuclear translocation of NFAT3. In the nucleus, NFAT3 homodimerizes or cooperates with partners like AP-1 (c-Fos/c-Jun), GATA3, or MEF2 to transactivate cytokine genes (IL-2, IL-4, TNF-α) and FasL at composite NFAT:AP-1 sites, while in cardiomyocytes, it drives pathological hypertrophy by inducing BNP and MHCα gene expression. Nuclear export and cytoplasmic sequestration are restored by rephosphorylation through GSK3β, CK1, or PKA. Uniquely, NFAT3 represses cell cycle progression and promotes apoptosis in neurons via Trim17 induction, in contrast to the pro-death role of NFAT4; deficiency of NFAT3 impairs Th2 differentiation and IgE responses. Dysregulated nuclear hyperactivation of NFAT3 contributes to rheumatoid arthritis synovial inflammation, cardiac hypertrophy and failure under pressure overload, and B cell lymphomas through constitutive IL-2 signaling. |
| References |
|---|
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.