- Inhibitors
- Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
JunD Antibody [K7H15]
Cat.No.: F4861
Application:
Reactivity:
Usage Information
| Dilution |
|---|
|
| Application |
|---|
| WB, IHC, IF |
| Reactivity |
|---|
| Mouse, Rat, Human |
| Source |
|---|
| Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody |
| Storage Buffer |
|---|
| PBS, pH 7.2+50% Glycerol+0.05% BSA+0.01% NaN3 |
| Storage (from the date of receipt) |
|---|
| -20°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles), 2 years |
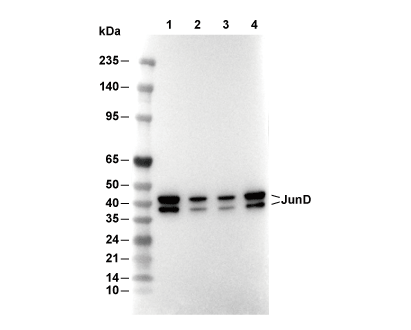
| Predicted MW Observed MW |
|---|
| 35 kDa 39 kDa,42 kDa |
| *Why do the predicted and actual molecular weights differ? The following reasons may explain differences between the predicted and actual protein molecular weight. |
| Positive Control | Human fetal brain; Human fetal liver; Human mammary gland tissue; Human fetal heart; Human lung squamous cell carcinoma tissue; Mouse cerebral cortex tissue; Rat cerebral cortex tissue; Human fetal kidney; HeLa cells; 293T cells; Jurkat cells; Raw264.7 cells; PC12 cells; NIH 3T3 cells |
|---|---|
| Negative Control |
Biological Description
| Specificity |
|---|
| JunD Antibody [K7H15] detects endogenous levels of total JunD protein. |
| Clone |
|---|
| K7H15 |
| Synonym(s) |
|---|
| Transcription factor JunD; Transcription factor AP-1 subunit JunD; JUND |
| Background |
|---|
| JunD is the most stable and least homologous AP-1 family bZIP transcription factor. It contains N-terminal transactivation domains A1 and A2 with JNK/SAPK phospho-acceptor sites (Ser69, Thr89, Thr91) that regulate activity in response to stress and growth factors. The protein has a divergent transrepression δ domain that enables anti-proliferative dominance, and a C-terminal bZIP module consisting of a basic region that inserts into the TGAGTCA TRE major groove and a leucine zipper that forms Y-shaped α-helical dimers with FosB, ATF2, or CREB. JunD:Fos heterodimers can displace c-Jun from proliferative TREs, repressing genes like cyclin D1 and p16^INK4a in Ras-transformed cells via δ domain steric occlusion, while also activating antioxidant and DNA repair/apoptosis genes such as VEGF and GADD45α/γ. The intronless junD gene allows rapid production of the ΔJunD splice variant, which lacks A1 and is less efficiently phosphorylated by JNK, resulting in weaker activation. JunD binds CREB sites in its own promoter to repress ZO-1 transcription and translation, destabilizing mRNA via 3'UTR-TIAR interaction and weakening epithelial barrier integrity. JunD knockout mice are viable but exhibit cardiomyocyte hypertrophy from derepressed IGF-I/ERK, stunted long-bone growth due to VEGF/FGF deficits, and infertility. Somatic amplification of JunD drives androgen-independent prostate cancer through AR crosstalk and restrains senescence in fibroblasts. Knockdown of JunD induces GADD45-mediated apoptosis and reduces prostate cancer xenograft growth. |
| References |
|---|
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.