- Inhibitors
- Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
JARID1A Antibody [E24E4]
Cat.No.: F4852
Application:
Reactivity:
Usage Information
| Dilution |
|---|
|
| Application |
|---|
| WB, IP, IF, FCM |
| Reactivity |
|---|
| Mouse, Human |
| Source |
|---|
| Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody |
| Storage Buffer |
|---|
| PBS, pH 7.2+50% Glycerol+0.05% BSA+0.01% NaN3 |
| Storage (from the date of receipt) |
|---|
| -20°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles), 2 years |
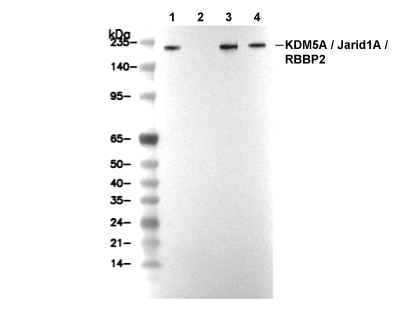
| Predicted MW Observed MW |
|---|
| 161 kDa, 22-46 kDa 162-240 kDa, 43 kDa |
| *Why do the predicted and actual molecular weights differ? The following reasons may explain differences between the predicted and actual protein molecular weight. |
| Positive Control | Mouse testis; HEK-293 cells; NIH/3T3 cells; HeLa cells; LLC cells; HAP1 cells |
|---|---|
| Negative Control |
Biological Description
| Specificity |
|---|
| JARID1A Antibody [E24E4] detects endogenous levels of total JARID1A protein. |
| Clone |
|---|
| E24E4 |
| Synonym(s) |
|---|
| JARID1A; RBBP2; RBP2; KDM5A; Lysine-specific demethylase 5A; Histone demethylase JARID1A; Jumonji/ARID domain-containing protein 1A; Retinoblastoma-binding protein 2; [histone H3]-trimethyl-L-lysine(4) demethylase 5A; RBBP-2 |
| Background |
|---|
| JARID1A (also known as KDM5A or RBP2), a JmjC domain-containing histone H3K4 demethylase, plays a pivotal role in epigenetic regulation by removing di- and tri-methyl marks from H3K4 to repress transcription at active promoters, featuring a multi-domain architecture including an N-terminal JmjN domain for catalytic coordination with the core JmjC domain requiring Fe(II) and α-ketoglutarate, an intervening ARID domain that binds GC-rich DNA motifs like CCGCCC via its L1 loop to target nucleosomes, PHD1-3 fingers where PHD1 recognizes unmodified H3K4 to stabilize repression in a feed-forward loop, a C5HC2 zinc finger enhancing demethylase activity, and plant homeodomain fingers facilitating histone tail interactions. JARID1A interacts with RB to enforce E2F repression during G1/S transition, joins NuRD and SIN3B complexes to coordinate deacetylation and remodeling via CHD4 for cell cycle gene control, accumulates at γ-H2AX foci post-DNA damage to reduce H3K4me3 without impairing double-strand break repair, and modulates circadian rhythm by enhancing CLOCK-BMAL1 cyclic transcription independently of demethylation, while in hematopoiesis it binds GATA1 via PHD2 to drive erythroid differentiation and proliferation, with NUP98-JARID1A fusions driving myeloid leukemia through aberrant H3K4 demethylation and pathway activation. Its overexpression promotes cancer progression by sustaining PI3K/Akt signaling via PTEN suppression, advancing the G1/S phase through Cyclin D1 upregulation and repressing let-7e miRNA, and inducing drug-tolerant states via HDAC interplay. |
| References |
|---|
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.