- Inhibitors
- Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
JAK3 Antibody [M5G12]
Cat.No.: F4827
Application:
Reactivity:
Usage Information
| Dilution |
|---|
|
| Application |
|---|
| WB, IP, IHC, IF, FCM |
| Reactivity |
|---|
| Human |
| Source |
|---|
| Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody |
| Storage Buffer |
|---|
| PBS, pH 7.2+50% Glycerol+0.05% BSA+0.01% NaN3 |
| Storage (from the date of receipt) |
|---|
| -20°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles), 2 years |
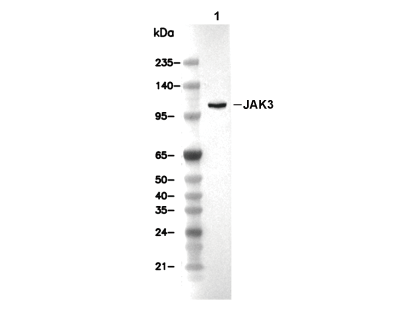
| Predicted MW Observed MW |
|---|
| 125 kDa 125 kDa |
| *Why do the predicted and actual molecular weights differ? The following reasons may explain differences between the predicted and actual protein molecular weight. |
| Positive Control | Human NK cell lymphoma tissue; Human large B cell lymphoma tissue; TF-1 cells; KARPAS-299 cells; HEL cells; Jurkat cells |
|---|---|
| Negative Control | HaCaT cells |
Biological Description
| Specificity |
|---|
| JAK3 Antibody [M5G12] detects endogenous levels of total JAK3 protein. |
| Clone |
|---|
| M5G12 |
| Synonym(s) |
|---|
| Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK3; Janus kinase 3; Leukocyte janus kinase; JAK-3; L-JAK; JAK3 |
| Background |
|---|
| JAK3 is a hematopoietic-specific Janus kinase that plays a vital role in cytokine signaling mediated by γc-chain receptors such as those for IL-2, IL-4, IL-7, IL-9, IL-15, and IL-21. It is constitutively associated with the intracellular domains of these receptors and, upon cytokine stimulation, undergoes transphosphorylation that activates its C-terminal kinase domain (JH1), while its N-terminal pseudokinase domain (JH2) provides autoinhibitory regulation through control of the activation loop. Ligand binding triggers JAK3 to autophosphorylate receptor tyrosines, creating SH2-docking sites for STAT proteins (STAT5, STAT3, STAT1), which JAK3 phosphorylates to initiate their dimerization, nuclear entry, and transcriptional activation of genes governing T, B, and NK cell development, survival, and differentiation, including Th1 and Th17 lineages. Mutations in the JH2 domain, such as V722I and G825A, can disrupt autoinhibition and result in gain-of-function activity leading to acute lymphoblastic leukemia, while deletions in the SH2-JH1 linker region also increase basal kinase activity. JAK3 loss-of-function mutations cause severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) due to failed lymphopoiesis, whereas somatic gain-of-function mutations drive malignancies such as T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia, acute myeloid leukemia, and large granular lymphocytic leukemia via persistent STAT activation. |
| References |
|---|
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.