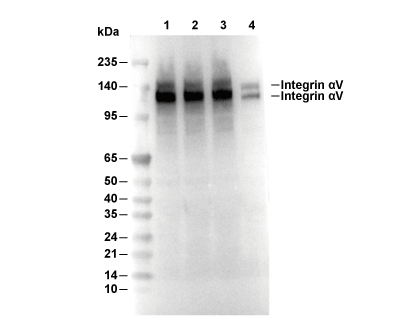
| Integrin αV, encoded by the ITGAV gene, is a versatile integrin alpha subunit that forms heterodimers with β1, β3, β5, β6, or β8 subunits, mediating cell-extracellular matrix (ECM) adhesion by recognizing RGD motifs in ligands such as vitronectin, fibronectin, and osteopontin, and playing key roles in cell migration, signaling, and tissue remodeling. The type I transmembrane glycoprotein features a large extracellular domain with a seven-bladed β-propeller head (lacking an I-domain), thigh, and two calf domains organized in a bent, low-affinity resting conformation that transitions to an extended, high-affinity state upon inside-out activation via talin/kindlin binding to its short cytoplasmic tail. The ligand-binding pocket is formed at the αV propeller-βI domain interface and is stabilized by metal ion sites (MIDAS, ADMIDAS, SyMBS on β; Ca²⁺ sites on αV genu/propeller). αV integrins regulate proliferation, survival, and migration through outside-in signaling via FAK/Src, PI3K/Akt, and MAPK/ERK pathways, with specific heterodimers mediating angiogenesis (αVβ3/β5 in endothelium), TGF-β activation (αVβ6/β8 in fibrosis and immunity), and osteoclast-mediated bone resorption (αVβ3). Dysregulation of αV integrins drives tumor progression, metastasis, and therapeutic resistance in cancers (pancreatic, glioblastoma, breast), contributes to pulmonary fibrosis and osteoporosis, and facilitates viral entry (adenovirus, SARS-CoV-2), establishing αV as a validated therapeutic target for antibodies and RGD mimetics in oncology and antifibrotic treatments. |