- Inhibitors
- Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
IKZF3 Antibody [D19G22]
Cat.No.: F4871
Application:
Reactivity:
Usage Information
| Dilution |
|---|
|
| Application |
|---|
| WB, IHC, IF, FCM |
| Reactivity |
|---|
| Mouse, Rat, Human |
| Source |
|---|
| Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody |
| Storage Buffer |
|---|
| PBS, pH 7.2+50% Glycerol+0.05% BSA+0.01% NaN3 |
| Storage (from the date of receipt) |
|---|
| -20°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles), 2 years |
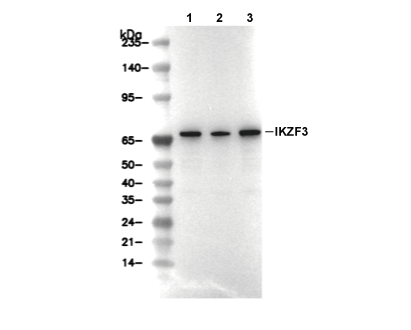
| Predicted MW Observed MW |
|---|
| 58 kDa 70 kDa |
| *Why do the predicted and actual molecular weights differ? The following reasons may explain differences between the predicted and actual protein molecular weight. |
| Positive Control | Human spleen tissue; Mouse cardiac muscle tissue; Rat spleen tissue; Human thymus cells; Jurkat cells; Raji cells; Ramos cells |
|---|---|
| Negative Control |
Biological Description
| Specificity |
|---|
| IKZF3 Antibody [D19G22] detects endogenous levels of total IKZF3 protein. |
| Clone |
|---|
| D19G22 |
| Synonym(s) |
|---|
| ZNFN1A3; IKZF3; Zinc finger protein Aiolos; Ikaros family zinc finger protein 3 |
| Background |
|---|
| IKZF3 (Aiolos) is a hematopoietic-specific zinc finger transcription factor from the Ikaros family, essential for B-cell development and effector maturation. It contains an N-terminal DNA-binding domain with four tandem C2H2 zinc fingers that recognize the core GGAAA motif, particularly through major groove contacts made by key arginine and histidine residues, and a C-terminal dimerization domain with two additional zinc fingers that enable homo- and heterodimerization with other Ikaros proteins such as IKZF1 (Ikaros), IKZF2 (Helios), and IKZF4 (Eos), facilitating both repressive and activating transcriptional complexes. IKZF3 orchestrates sequential B-cell programming: initial IKZF1 homodimers establish lymphoid priming, while IKZF1:IKZF3 heterodimers recruit chromatin remodeling and co-repressor complexes such as NuRD, SWI/SNF, and PRC2 to silence pro-apoptotic genes and enforce survival checkpoints. As B cells mature, IKZF3 homodimers activate key regulators like BLIMP1, STAT3, and XBP1 to drive plasma cell differentiation and antibody secretion. In regulatory T cells, IKZF3 modulates IL-10 expression indirectly through synergy with FOXP3. Germline dominant-negative IKZF3 variants can interfere with IKZF1 function, repressing genes involved in B and T cell homing and leading to immunodeficiency, while somatic overexpression of IKZF3 sustains aberrant BCR and IL-7R signaling in leukemias. |
| References |
|---|
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.