- Inhibitors
- Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
HEF1/NEDD9 Antibody [M16B3]
Cat.No.: F4740
Application:
Reactivity:
Usage Information
| Dilution |
|---|
|
| Application |
|---|
| WB, IP |
| Reactivity |
|---|
| Human, Mouse, Rat, Monkey |
| Source |
|---|
| Mouse Monoclonal Antibody |
| Storage Buffer |
|---|
| PBS, pH 7.2+50% Glycerol+0.05% BSA+0.01% NaN3 |
| Storage (from the date of receipt) |
|---|
| -20°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles), 2 years |
| Predicted MW |
|---|
| 105 kDa, 115 kDa |
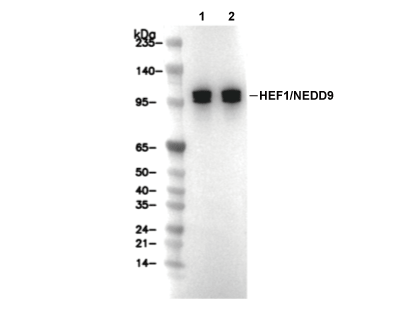
| Positive Control | A549 cells; C2C12 cells |
|---|---|
| Negative Control |
Biological Description
| Specificity |
|---|
| HEF1/NEDD9 Antibody [M16B3] detects endogenous levels of total HEF1/NEDD9 protein. |
| Clone |
|---|
| M16B3 |
| Synonym(s) |
|---|
| NEDD9; hEF1; CRK-associated substrate-related protein (CAS-L; CasL); Cas scaffolding protein family member 2 (CASS2); NEDD-9; Renal carcinoma antigen NY-REN-12; p105; Enhancer of filamentation 1 p55; CASL |
| Background |
|---|
| HEF1, also known as NEDD9 or Cas-L, is a key multidomain adaptor protein within the Cas family, coordinating integrin-mediated signaling at focal adhesions during interphase and localizing to centrosomes and mitotic structures in G2/M phase to regulate cell adhesion, migration, polarity, and survival. HEF1 contains an N-terminal SH3 domain (residues 3–65) for binding proline-rich proteins, a substrate domain (residues 110–356) enriched in tyrosine motifs such as Y189 and Y214 that are phosphorylated by Src and FAK to recruit SH2 domain-containing effectors like Crk and Abl, a serine-rich region (residues 357–560) forming a four-helix bundle for structural stability and protein interactions, and a C-terminal focal adhesion targeting (FAT) domain (residues 561–834) with helix-loop-helix motifs that facilitate FAK docking, Src binding, and dimerization. HEF1 integrates signals from FAK, Src, PDGFR, and Abl, leading to phosphorylation of its substrate domain and assembly of signaling complexes that promote actin cytoskeleton remodeling, focal adhesion turnover, invadopodia formation via MMP9 secretion, and activation of pathways such as FAK-Src-Aurora-A for chemotaxis and mitotic progression; its phosphorylation dynamics further regulate apoptosis resistance and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. NEDD9 overexpression drives metastasis in cancers like glioblastoma, melanoma, and lung carcinoma by enhancing invasion and survival signaling, while deficiency impairs tumor progression and leukocyte migration. |
| References |
|---|
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.